In this blog post, I will show you the steps to fix CVE-2022-30190 vulnerability Using Microsoft Intune. On Monday, May 30, 2022, Microsoft issued CVE-2022-30190 regarding the Microsoft Support Diagnostic Tool (MSDT) in Windows vulnerability.
A remote code execution vulnerability exists when MSDT uses the URL protocol from a calling application, such as Word. An attacker who successfully exploits this vulnerability can run arbitrary code with the privileges of the calling application. The attacker can then install programs, view, change, or delete data, or create new accounts in the context allowed by the user’s rights.
At the time of writing this blog post, Microsoft has not released a patch to fix this issue, but it has suggested a workaround: disable the MSDT URL protocol. Disabling the MSDT URL protocol prevents troubleshooters from being launched as links, including links throughout the operating system.
Most of the Windows Client and Server Operating Systems are impacted. For full information, follow the Microsoft advisory link: https://msrc.microsoft.com/update-guide/en-US/vulnerability/CVE-2022-30190.
Contents
Workaround
The Workaround to fix this vulnerability immediately is to delete the ms-msdt registry key. If you have a couple of machines to fix this vulnerability on, you can simply open the registry editor on each PC, browse to HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT, find ms-msdt, and delete this key. Alternatively, you can open a command prompt as an administrator on each PC and type the commands below.
The first line of the command will back up the registry key ms-msdt, and the second line of the code will delete the registry key.
reg export HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt msdtregkeybackup.reg reg delete HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt /f
Delete msdtregbackup Registry key using Intune
If you use Microsoft Intune to manage all your organization devices, you can create a PowerShell script and deploy it via Intune. I have created the below PowerShell script and saved it in a file called msdtregfix.ps1.
if(Test-path C:\msdtregbackup)
{
reg export HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt C:\msdtregbackup\msdtkey.reg /y
reg delete HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt /f
}
else
{
New-item "C:\msdtregbackup" -itemtype Directory
reg export HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt C:\msdtregbackup\msdt.reg /y
reg delete HKEY_CLASSES_ROOT\ms-msdt /f
}
Deploy a PowerShell Script from Intune
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > Scripts and remediations > Platform scripts.
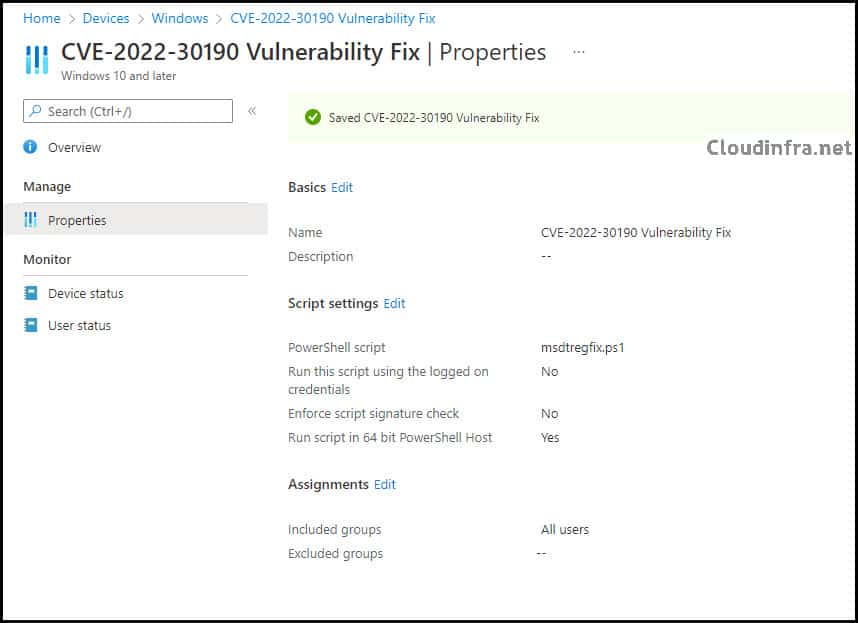
- Click on Add > Type any suitable Name, for example: CVE-2022-30190 Vulnerability Fix.
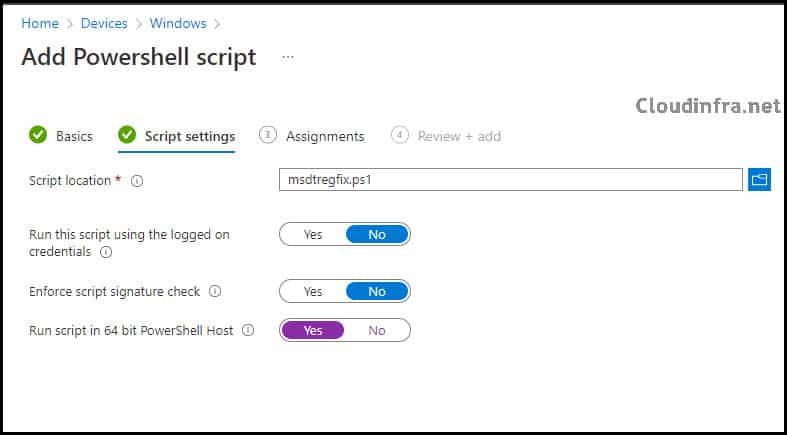
- Script Location: Browse to your PowerShell Script
- Run this script using the logged-on credentials: No
- Enforce script signature check: No
- Run script in 64-bit PowerShell Host: Yes
- Assignments: Assign your script to an Entra Security Group and add Windows devices.
- Review + add: Review the deployment summary and click add.
How to Deploy a PowerShell Script using Intune.
Step-by-step guide
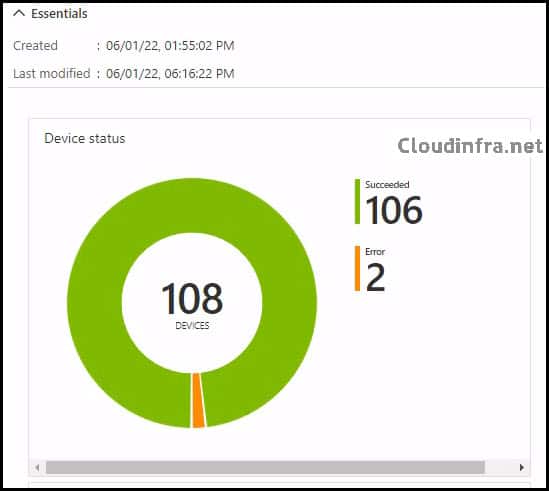
- Results of the script deployment.
Conclusion
In this blog post, you have seen how to fix Vulnerability CVE-2022-30190 on Windows devices. Apart from that, you have also learned how to manually delete a registry key and use Microsoft Intune.
Vulnerability CVE-2023-38408 and CVE-2023-28531 on enterpriseregistration cname
During the configuration of our Microsoft 365 (M365) Software as a Service (SaaS) environment, we implemented a CNAME record (enterpriseregistration.capitecbank.co.za) to enable auto-discovery for the Intune enrollment service, in accordance with Microsoft’s guidelines. Our cybersecurity team has flagged this URL as an external-facing entity potentially susceptible to vulnerabilities CVE-2023-28531 and CVE-2023-38408, which are associated with tcp port 22 and issues related to ssh-add (OpenSSH/OpenBSD). This situation is impacting our security posture assessment, and as a financial institution, we aim to uphold a high security rating.