In this guide, I will demonstrate the steps to onboard windows devices to Defender for Endpoint via Intune. You can also manually onboard devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) using an onboarding package, which is a CMD script file (WindowsDefenderATPLocalOnboardingScript.cmd). To use this method, download the package from the Defender portal > Settings > Endpoints > Device management > Onboarding, and then run it on the device you want to onboard.
Microsoft suggests using this onboarding method only if you have a limited number of devices (between 1 and 10). For bulk deployment, use Intune, Group Policy, or Configuration Manager.
Microsoft Defender provides enterprise-grade endpoint detection and response (EDR), advanced threat protection, attack surface reduction, endpoint vulnerability management, and automated investigation and remediation. For more information on Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE), refer to this link: Microsoft Defender for Endpoint | Microsoft Learn.
About Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Contents
Prerequisites
- Devices must be enrolled into Intune.
- Defender for Endpoint Plan 1 or Plan 2. You can use either license for onboarding, for difference between the two, refer here: Plan1 vs. Plan2. Plan 1 is included in Microsoft 365 E3/A3/G3 or buy standalone. Plan 2 is included with Microsoft 365 E5/A5/G5, Microsoft 365 E5 Security, Windows Enterprise E5, or buy standalone.
- Microsoft 365 business premium includes Defender for business (designed for small to medium (SMB) enterprises: up to 300 employees).
- To onboard servers to defender, you will need any of the following licenses:
- Microsoft Defender for Servers Plan 1 or Plan 2.
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint Server.
- Microsoft Defender for Business servers.
- Windows OS (Client and Server) support: Windows versions supported by defender.
- Non-Windows OS supported by Defender for Endpoint:
- Mac (client devices)
- Linux
- Windows Subsystem for Linux
- Android
- iOS
- Last but not least, you will need Intune admin and Defender portal permissions.
I also recommend referring to Microsoft’s defender’s minimum requirements page, which lists the complete set of requirements, including hardware, software, network, browser, and more.
Enable MDE ELAM Driver
If you are running Microsoft Defender Antivirus as the primary anti-malware product on your devices, no action is required. Defender agent will onboard normally. If you use a non-Microsoft antivirus (like McAfee, Symantec etc.) with MDM or Configuration Manager, ensure that the Microsoft Defender Antivirus Early Launch Antimalware (ELAM) driver is enabled. Which is its default state anyway, but if you get any issues, then do a quick check to confirm it.
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (the EDR/XDR agent) depends on ELAM to initialize properly at boot and require that ELAM driver is loaded during startup (for Defender, that’s WdBoot.sys). If a system policy (like a Group Policy, Intune setting, registry key, or a bcdedit flag) disables ELAM, then the Defender for Endpoint agent may fail to onboard or may run with reduced functionality.
Few things you can check
- Check if a Group policy is not configuring Boot-Start Driver Policy to All drivers (value 7).
- Check if an Intune Policy is not setting Boot-Start Driver Policy to All drivers (value 7).
- Check and confirm
bcdeditflag disableelamdrivers is not set to Yes. If it’s set to Yes, that means ELAM is disabled. If this flag is set to no or the flag itself does not exist, ELAM is not disabled.
Step 1: Create a Service-to-Service Connection (One-Time)
First step is to create and establish a service-to-service connection between Intune and Defender for Endpoint. This connection enables Intune to interact with Microsoft Defender on the devices for installation of necessary packages, for onboarding devices to MDE, configuration of MDE client using Intune policies and getting the risk scores etc.
- Go to Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Click the link Open the Microsoft Defender Security Center.
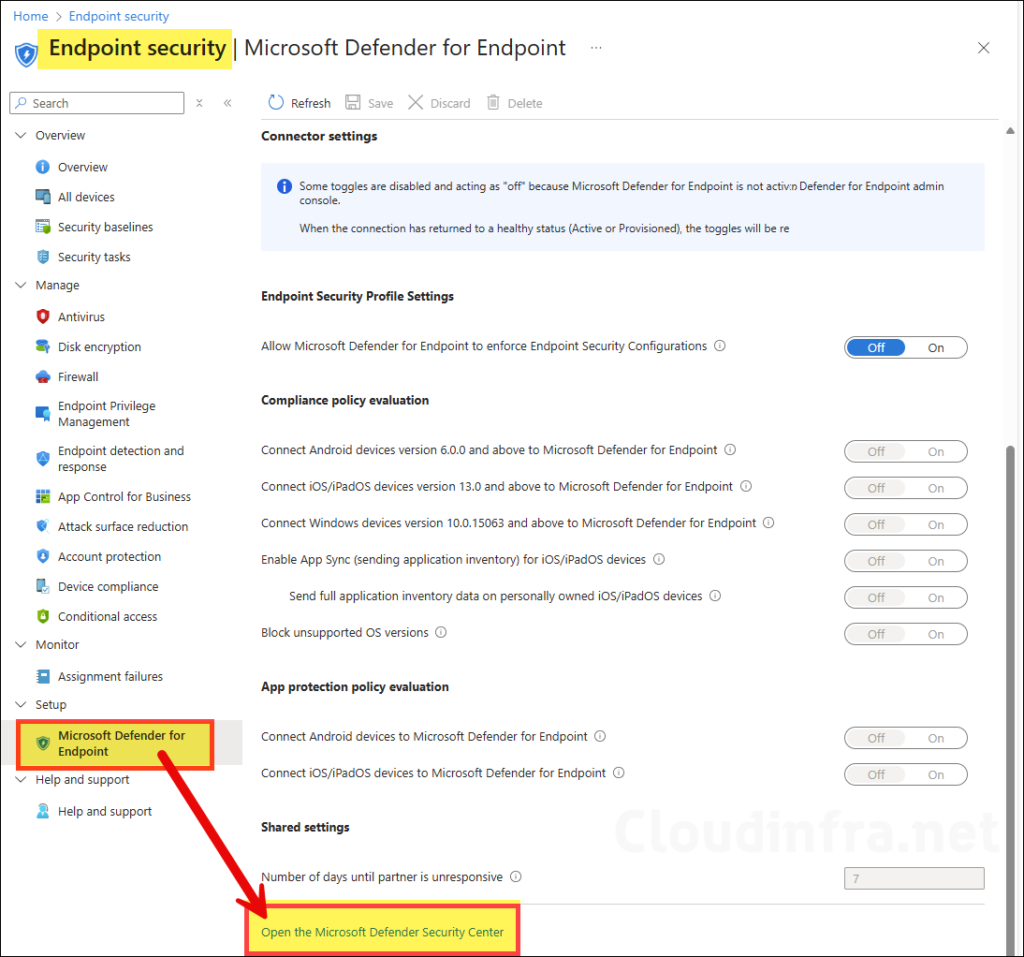
- Clicking on the link will open Microsoft Defender portal, If there are any issues, then use this direct link: Microsoft Defender Portal.
- Under System menu, go to Settings > Endpoints.
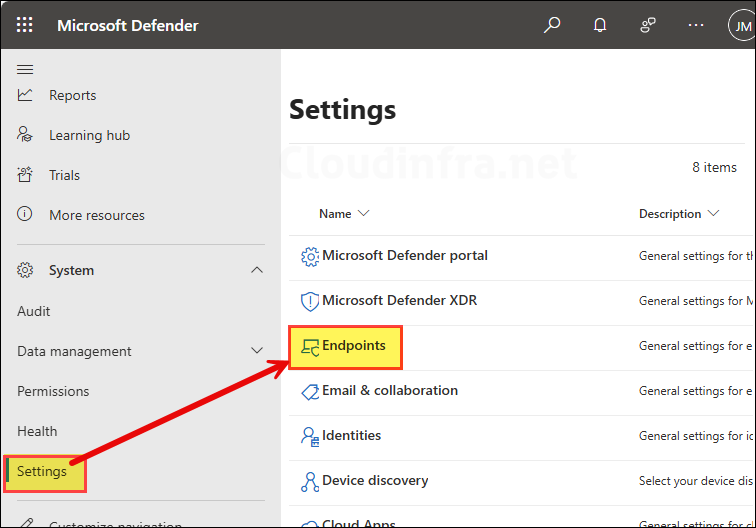
- Click on Advanced Features and enable the toggle switch next to Microsoft Intune connection, Click on Save preferences. That’s it!, you have created a service to service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Now go back to the Intune portal for rest of the configuration.
Note that the sync between Intune and defender occurs at least once every 24 hours. If there is an issue with this connection, then Intune will still accept the previous values of threat levels shared by defender for a number of days. This value can be changed here: Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint > Number of days until partner is unresponsive. After that, Intune will ignore device risk score values shared by defender.
Step 2: Back to the Intune Portal
Now, once the service-to-service connection is established, go to Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. The first thing you will notice is that the connection status changes from Unavailable to Available. You will also see the timestamp of the last synchronization between Defender and Intune. This confirms that Defender and Intune are successfully integrated.
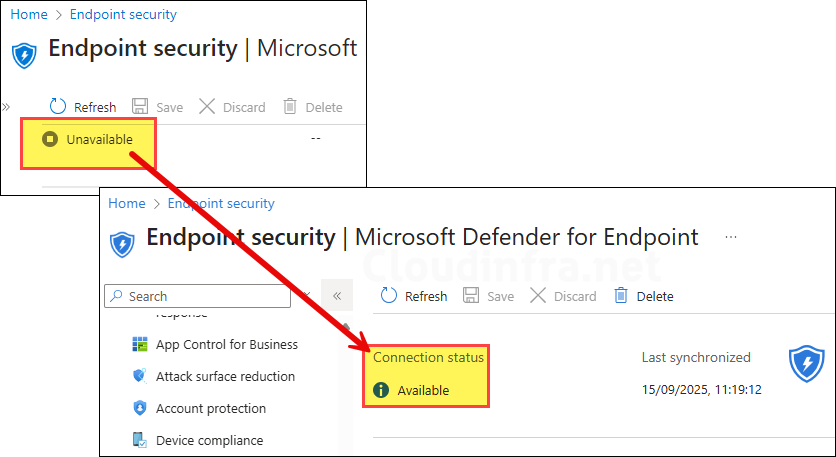
Step 3: Configure Defender for Endpoint Settings on Intune
In this step, you can configure the connection between different device platforms (e.g. Android, Windows, iOS etc.) and MDE using the toggle switches. This lets Intune receive security signals such as device risk scores (low, medium, high), which compliance policies can use to determine if a device is compliant. In a compliance policy, you would use Require the device to be at or under the machine risk score setting to utilize the risk scores.
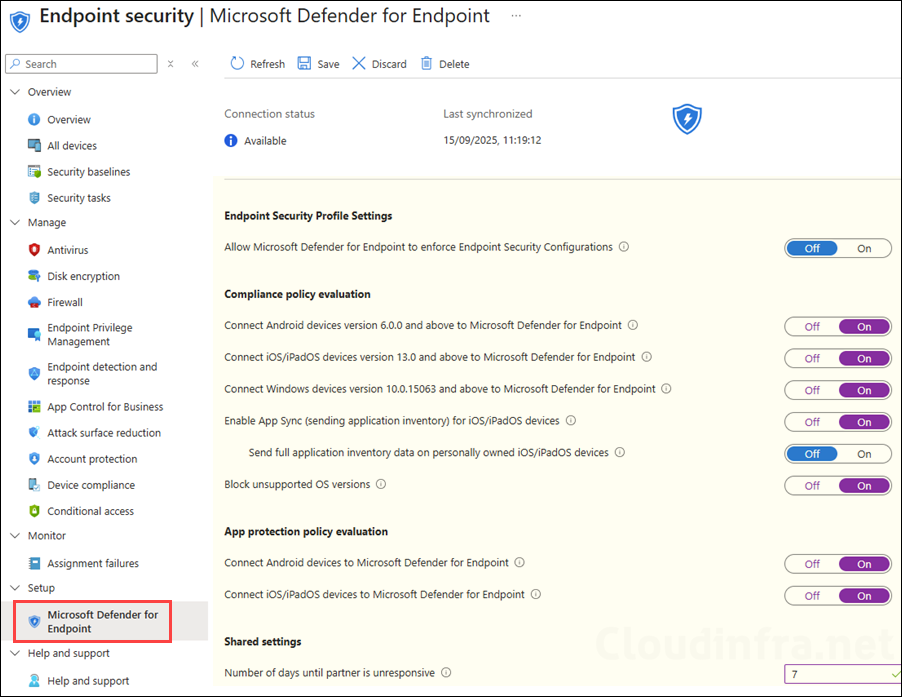
Go to Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Microsoft Defender for Endpoint and configure it according to your requirements. I have provided the details about each setting below to help you configure them correctly.
- Allow Microsoft Defender for Endpoint to enforce Endpoint Security Configurations: This lets Microsoft Defender for Endpoint enforce certain security configurations (like Defender Antivirus, Firewall, SmartScreen, Attack Surface Reduction, etc.) on devices that are onboarded to MDE but not enrolled in Intune. Microsoft refers to this scenario as Security Management for Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. I will keep this setting Off as all devices in my organization are enrolled and managed by Intune.
Compliance policy evaluation
Under Compliance policy evaluation, you can use the toggle switches to connect Android, iOS/iPadOS, and Windows devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE). When a toggle is set to On, Intune compliance policies that use the device threat level rule include MDE risk signals such as threat detections and risk scores in their evaluation, allows devices to be assessed for compliance.
When a toggle is set to Off, Intune ignores MDE risk data for those policies, and any devices previously marked noncompliant mainly because of MDE-reported risk score are re-evaluated and may become compliant.
- Connect Android devices version 6.0.0 and above to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: On
- Connect iOS/iPadOS devices version 13.0 and above to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: On
- Connect Windows devices version 10.0.15063 and above to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: On
- Enable App Sync (sending application inventory) for iOS/iPadOS devices: On
- Send full application inventory data on personally owned iOS/iPadOS devices: No (Keep Off for personal devices to respect privacy)
- Block unsupported OS versions: Yes
App protection policy evaluation
Enable the toggle switches for Android and iOS/iPadOS devices so that app protection policies (MAM) using the device threat level rule will evaluate devices based on the risk scores. When you keep this setting off, Intune will not use device risk details (sent over by this connector) during app protection policies calculation for policies with a Device threat level configured.
If you previously enabled this setting and used risk scores in app protection policies to evaluate devices, but now choose to disable it, Intune will stop considering the risk scores. As a result, any devices that were marked non-compliant primarily due to their risk score may become compliant.
- Connect Android devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: On
- Connect iOS/iPadOS devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint: On
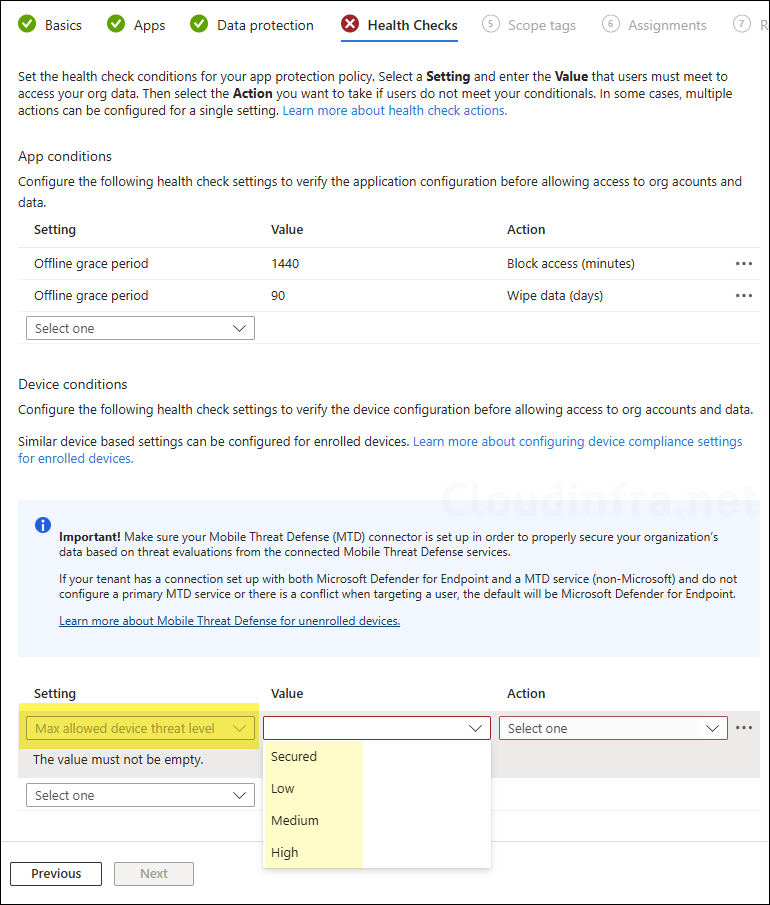
Below is a screenshot of an App protection policy where you can configure the Max allowed device threat level. This can be set to Secured, Low, Medium or High. For this to work, App protection policy evaluation defender connection must be on.
Shared settings
Under the shared settings, you can configure Number of days until partner is unresponsive value. The number can be from 1 to 365. This value is the continuous number of days when there is no service connection between Intune and Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) and Intune will then mark this connection as unresponsive. When the connectivity is lost and this threshold is expired, then Intune will ignore all risk scores from defender across every device in the tenant until the connection is restored.
- Number of days until partner is unresponsive: The default value is 7 days, but it can be set up to 365 days, which is not recommended. Using a higher value means Intune will continue to trust Defender risk scores even if the connection between Defender and Intune is lost, which can result in outdated or inaccurate compliance data.
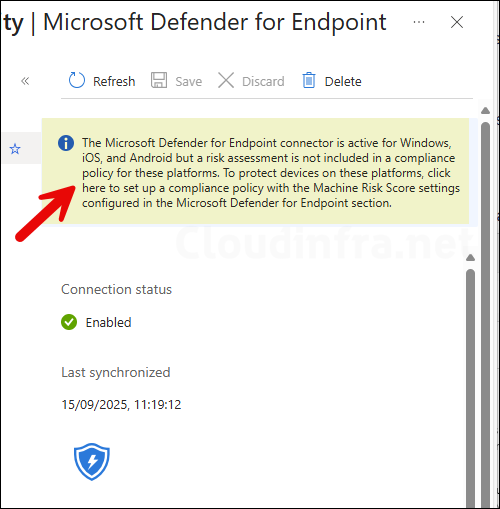
After configuring all the settings on the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint page, click Save to apply the changes. You may get an information message at the top of the page recommending that you include device risk assessments in your compliance policies.
The Microsoft Defender for Endpoint connector is active for Windows, iOS, and Android but a risk assessment is not included in a compliance policy for these platforms. To protect devices on these platforms, click here to set up a compliance policy with the Machine Risk Score settings configured in the Microsoft Defender for Endpoint section.
Information message on the Portal after clicking Save
Clicking on the message will open the Device compliance policies page, where you can review your existing policies and configure the setting Require the device to be at or under the machine risk score.
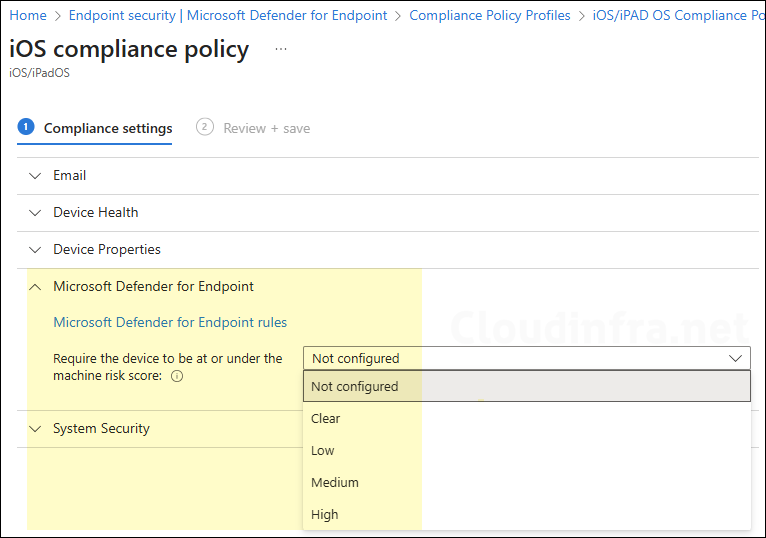
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint can classify a device as medium or high risk if a threat is detected. You can use an Intune compliance policy to mark high-risk devices as non-compliant, and create a conditional access policy to block those non-compliant devices from accessing company resources.
Step 3: Create an EDR Policy to Onboard Windows Devices
Now that we have set up a service-to-service connection and configured the Defender connection settings in the Intune portal, we can begin onboarding windows devices to defender. For onboarding, you need to create an EDR (Endpoint Detection and Response) policy which deploys a package/script on the target devices to onboard devices to defender.
Before creating a policy, check EDR Onboarding Status to find out the Onboarding status of each device. Go to Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > EDR Onboarding Status. Check the Onboarding status column.
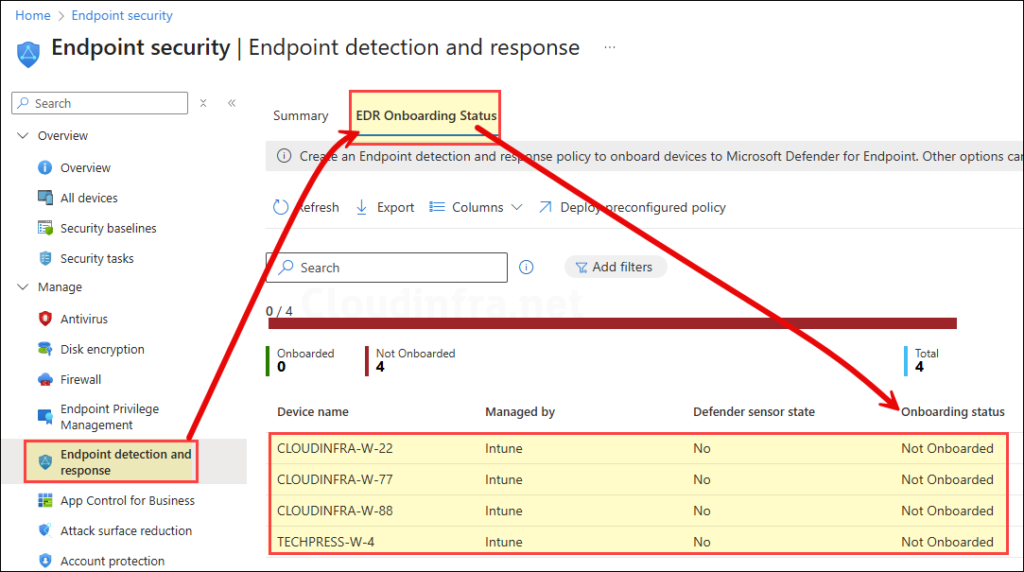
Now, let’s create an EDR policy to onboard the devices. There are two ways to create a policy. The first is a preconfigured EDR policy, which applies to all devices by default and cannot be scoped to a group. The second is a custom policy, which can be assigned to all devices or can be scoped to a specific group. Use one of these options to create a policy.
Option 1: Deploy preconfigured policy
To create a preconfigured policy to onboard All devices, Simply go to Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > EDR Onboarding Status > click Deploy preconfigured policy.
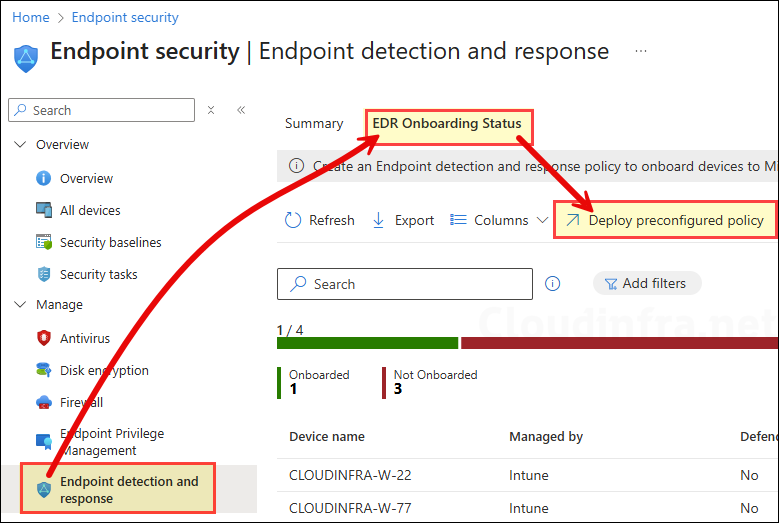
Option 2: Create a Custom EDR Policy
Follow below steps to create an EDR policy which also deploys a package/script to onboard devices to Defender, but can be scoped to a group of devices.
- Go to Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > click on Create policy.
- Select Platform as Windows and Profile as Endpoint detection and response. Click on Create.
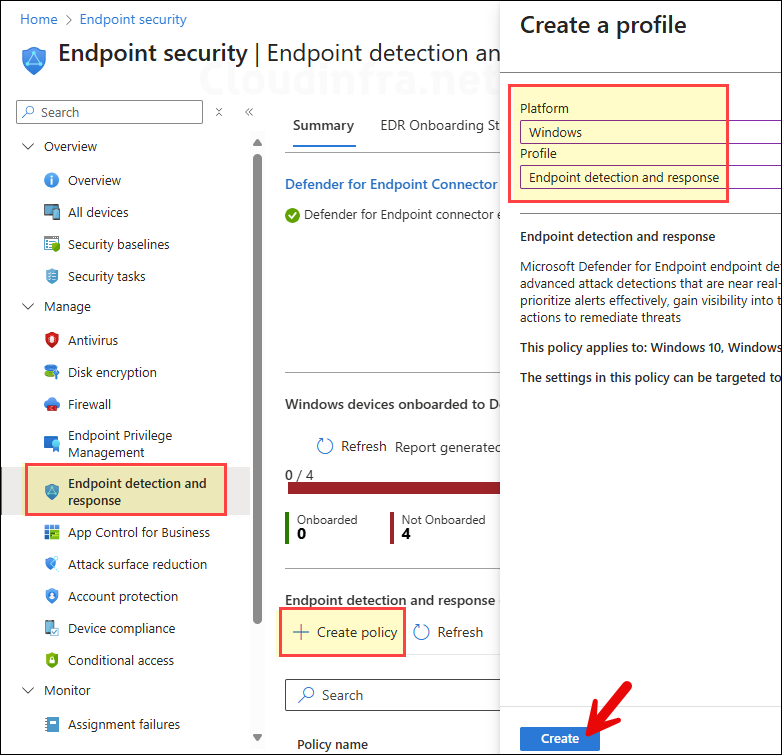
- Basics tab: Provide a name and description of the policy. For example: Onboarding Windows devices to Defender.
- Configuration settings:
- Microsoft Defender for Endpoint client configuration package type: Set this to Auto from connector. This allows intune to automatically use the onboarding package it received from defender. You will get this option only after successfully establishing Intune and defender service to service connection.
- Onboarding blob from Connector: pre-populated.
- Sample Sharing: This setting controls whether suspicious files from your devices can be automatically sent to Microsoft for deeper analysis. Select All (Default) which is recommended setting. If you do not want to send any files to Microsoft for analysis then select None.
- [Deprecated] Telemetry Reporting Frequency: Deprecated policy, keep it Not configured.
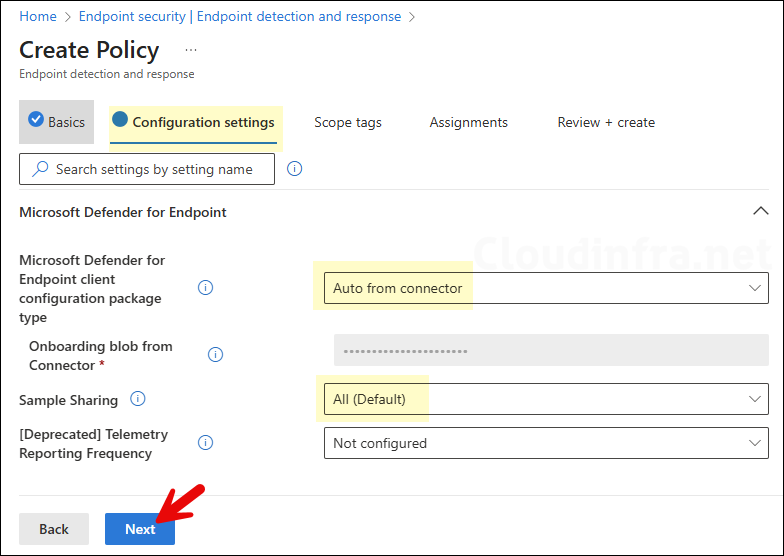
- Scope tags (optional): A scope tag in Intune is an RBAC label you add to resources (policies, apps, devices) to limit which admins can see and manage them. For more Information, read: How to use Scope tags in Intune.
- Assignments: Assign the policy to Entra security groups that contain the target users or devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + create: Review the deployment summary and click Create.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
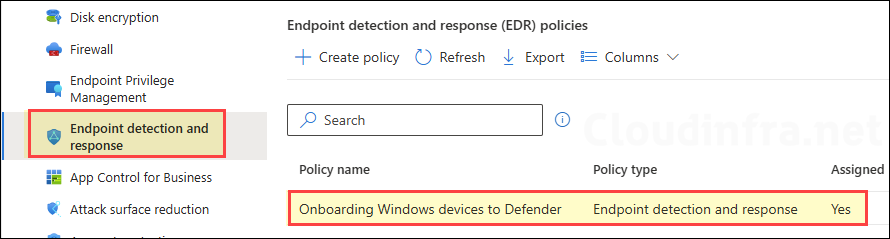
Monitoring EDR Policy
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response.
- Click to open the Onboarding Windows devices to Defender policy, and at the top of the page, you’ll see a quick view of the Success, Failure, Conflict, Not Applicable, and In Progress status.
- Click on View report to access more detailed information.

Step 4: Verify Device Onboarding Status
You can check the Onboarding status of devices on Intune admin center and also on Defender portal as well. Let’s check both the ways.
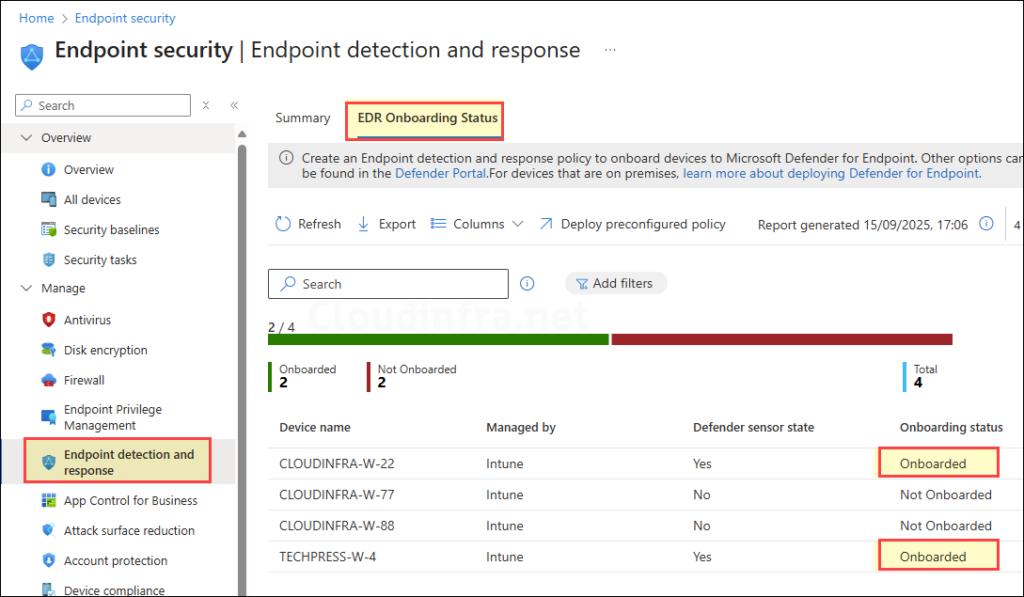
Check Device Onboarding status on Intune
Use Intune admin center to verify if the device is Onboarded to defender, let’s check the steps:
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Endpoint security > Endpoint detection and response > EDR Onboarding Status. Check the Onboarding status column, for devices which are successfully onboarded, the status should show as Onboarded.
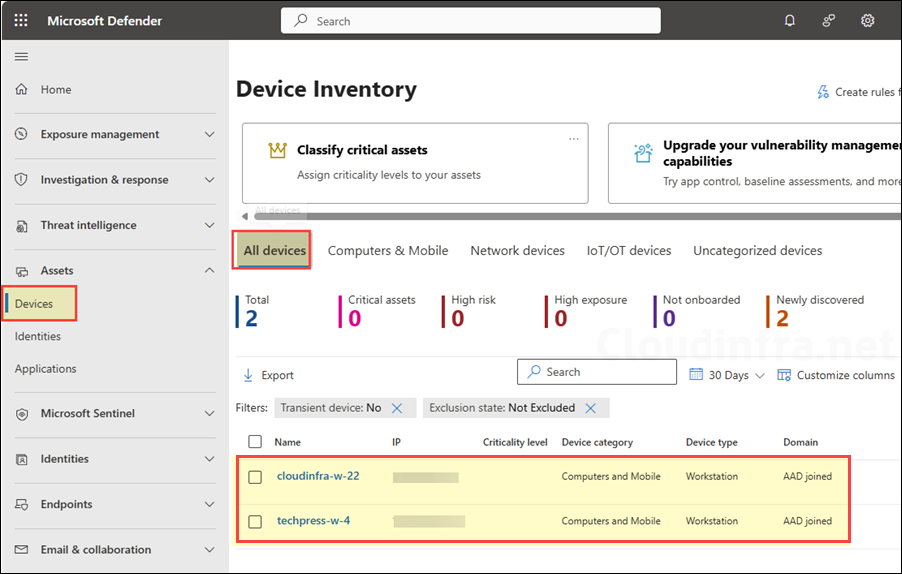
Check Device Onboarding status on Defender Portal
You can also use Microsoft Defender portal to verify if a device has been successfully onboarded.
- Go to Microsoft Defender portal > Assets > Devices. Under All devices you will find all the devices which are enrolled with Microsoft Defender for Endoint.
Conclusion
This blog post provided details on the steps to onboard Windows devices to Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) using Intune. You can also onboard macOS, iOS, Android, and Linux devices. Use the links below to learn more about onboarding non-Windows devices to Defender.