In this guide, I will show you the steps on how to implement applocker using Intune. Applocker consists of policies and rules designed to allow or deny app execution on Windows devices. It plays a vital role in increasing the security of all devices within your organization by controlling the execution of applications, scripts, DLL files, and packaged apps.
Requirements to use Applocker
- A device with Windows 10 or Windows 11 OS to prepare for Applocker rules.
- Application Identity service enabled.
Supported File Extensions in Applocker
- Executable files: .exe and .com
- Windows Installer files: .msi, mst, and .msp
- Scripts: .ps1, .bat, .cmd, .vbs, and .js
- DLLs: .dll and .ocx
- Packaged apps and packaged app installers: .appx and .msix.
Table of Contents
1. Create an Applocker Policy
To create an Applocker policy, you must log in as an administrator on a Windows 10 or Windows 11 device and follow these steps:
Enable Applocker
- Press Windows + R to open the Run Dialog box.
- Type secpol.msc and Press Enter.
- Expand Application Control Policies.
- Right-click AppLocker and select Properties.
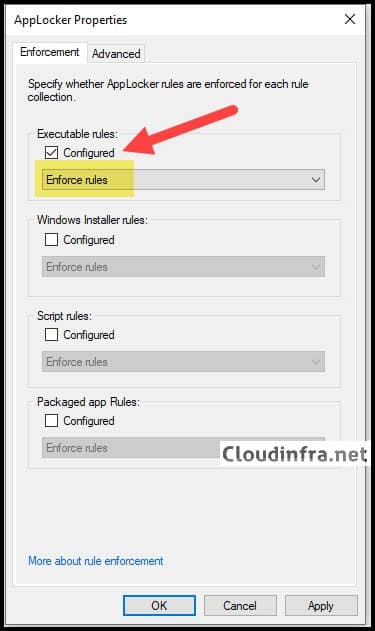
- Check the Configured box under the Executable rules section and select Enforce rules from the drop-down menu.
- Click on OK.
2. Add Applocker Default Rules
After we have enabled Applocker, you can proceed to create default Applocker rules. You can follow the below steps to create default applocker rules:
- Press Windows + R to open Run Dialog box.
- Type secpol.msc and Press Enter
- Expand Application Control Policies
- Expand AppLocker
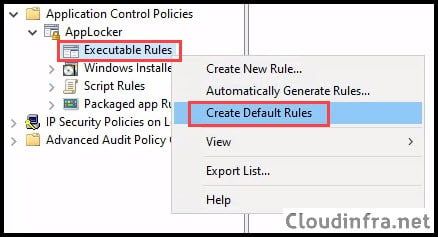
- Right-click on Executable Rules and click on Create Default Rules.
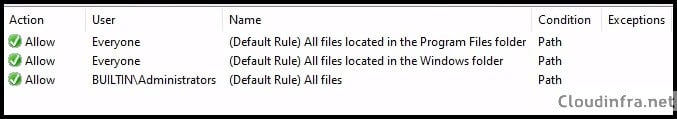
- Default rules ensure that executables are not blocked from C:\Program Files and C:\Windows folder. These folders contain applications installed on the device and OS files.
- A third default Allow rule is also created for Administrators. As per the default rule, administrators can execute all files from any location, and this policy does not restrict them.
3. Create Applocker Custom Rules
We can now create custom Applocker rules to prevent specific applications from running on the device. I will use a Google Chrome application as an example in the next steps.
- Press Windows + R to open Run Dialog box.
- Type secpol.msc and Press Enter.
- Expand Application Control Policies.
- Expand AppLocker.
- Right-click on Executable Rules and click on Create New Rule.
Click Next.
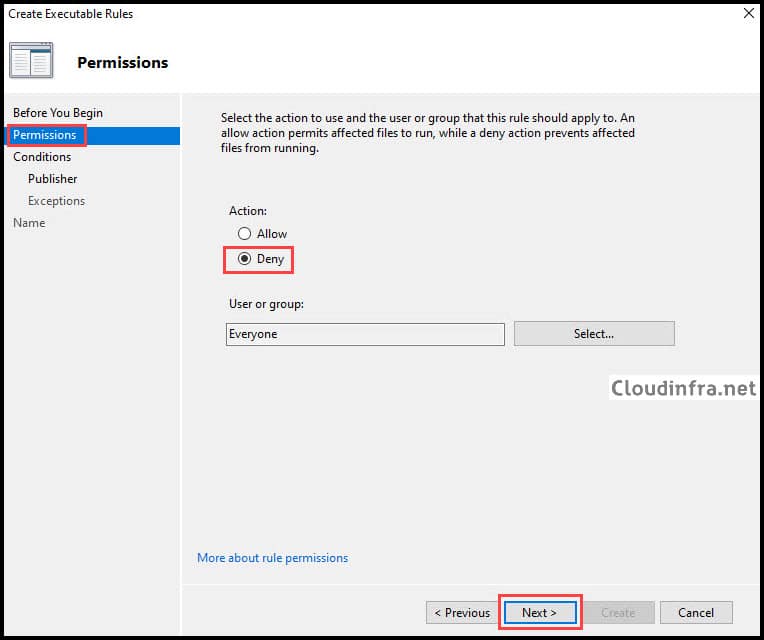
- Select Deny and click on Next.
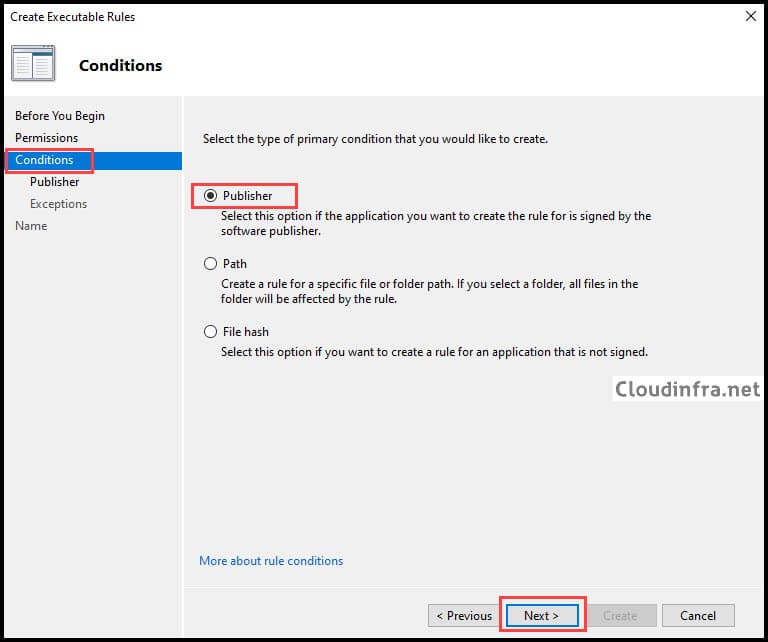
- Select Publisher and click on Next.
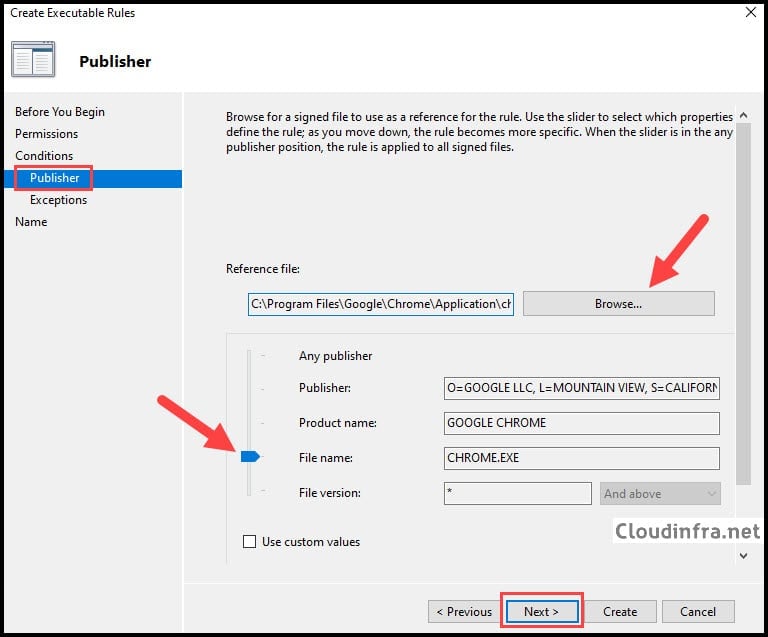
- Click on the Browse and select the application. For example, Google Chrome. It’s usually installed at C:\Program Files\Google\Chrome\Application location. Select the chrome.exe file.
- Move the slider to file name to generalize the File version. This means that this rule will apply to all versions of Google Chrome app.
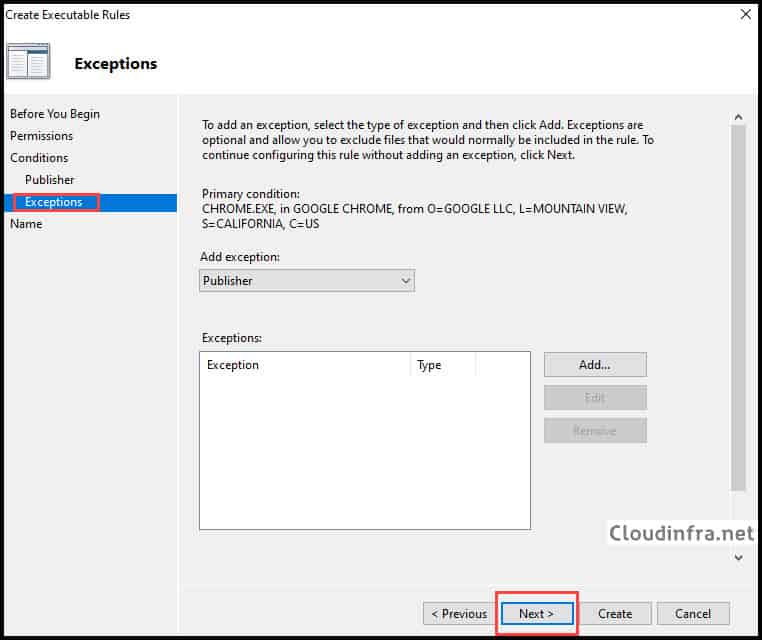
- On Exceptions window. Select Next.
- Provide a Name and Description to Identify this rule on the Applocker rules page.
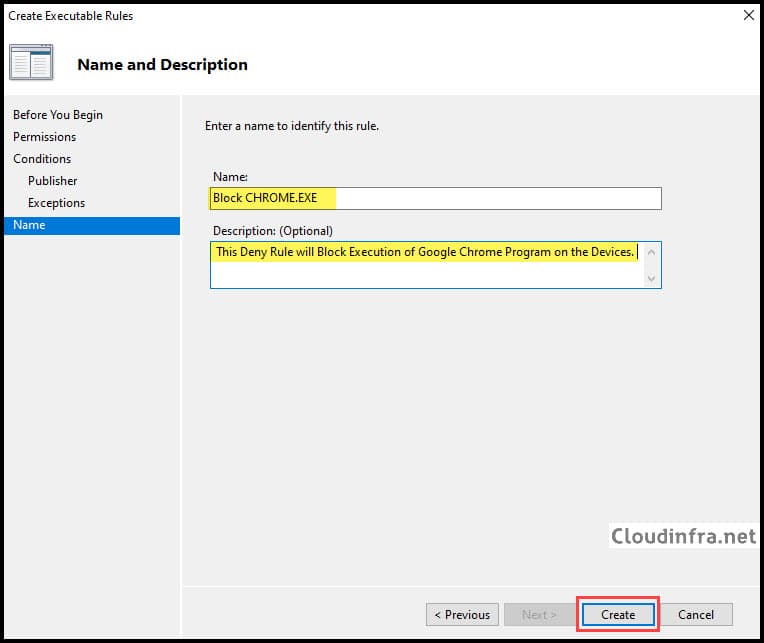
- The applocker rule has been created to deny the Google Chrome app.
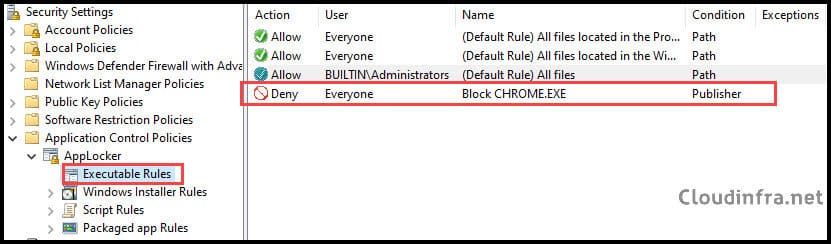
4. Export Applocker Rules
Now, we can export the rules from Applocker. Follow below steps to export the rules:
- Press Windows + R to open Run Dialog box.
- Type secpol.msc and Press Enter.
- Expand Application Control Policies.
- Right Click on AppLocker and select Export Policy.
- Save Applocker XML configuration file.
5. Deploy Applocker rules using Intune
You can follow below steps to deploy Applocker rules we exported in the previous step:
- Sign in to the Intune admin center. > Devices > Windows > Configuration > Create > New Policy.
- Select:
- Platform: Windows 10 and later
- Profile type: Templates
- Template Name: Custom
- Provide a Name and Description, and click on Next.
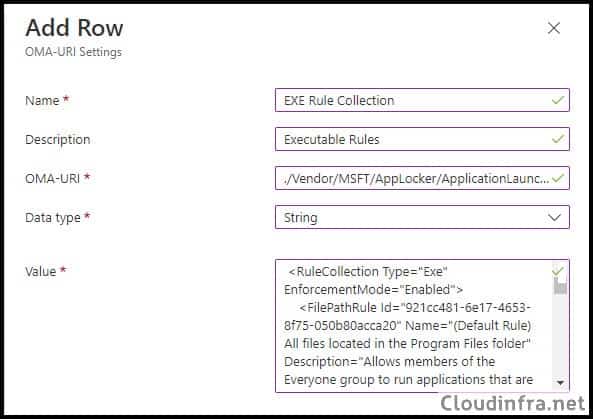
- Click on Add and add the OMA-URI setting:
- Name: EXE Rule Collection (You can provide whatever name you like)
- Description: Executable Rules
- OMA-URI: ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/EXE/Policy
- Data type: String
- Value: Copy and Paste XML file content from <RuleCollection Type> to </RuleConnection>
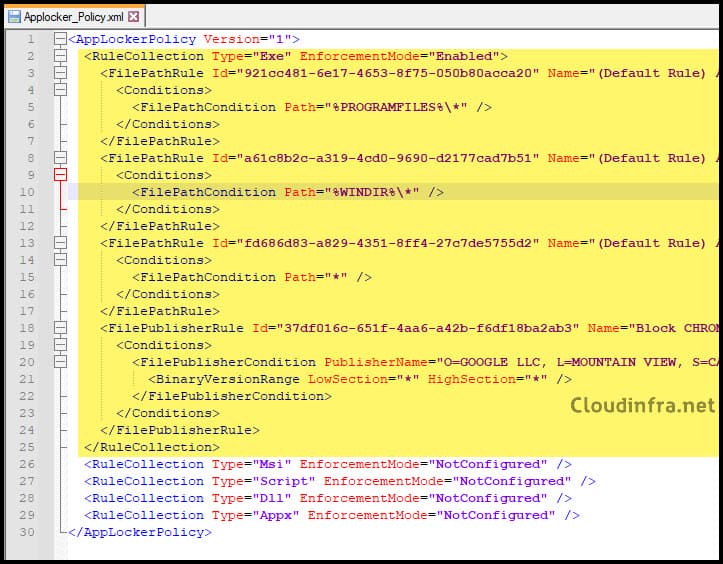
- OMA-URI setting configured on Intune admin center.
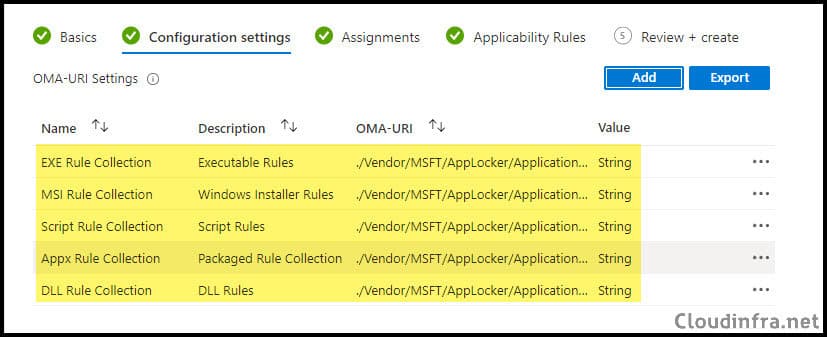
- You can also create other Applocker policies and use the OMA-URI setting below to deploy them using Intune.
- ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/MSI/Policy
- ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/Script/Policy
- ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/StoreApps/Policy
- ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/DLL/Policy
- Click on Save and Next.
- Scope tags, click Next.
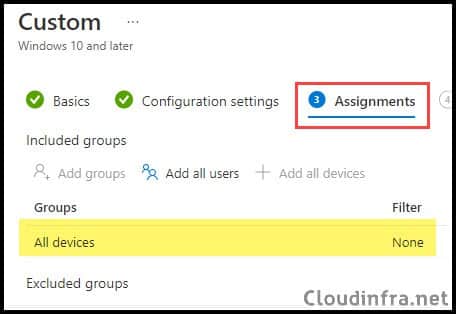
- Assignments: Select an Entra security group containing Windows devices. You can also click on Add all devices or All users. Click Next.
- Applicability Rules: click Next.
- Review and Create, click Create.
End User Experience
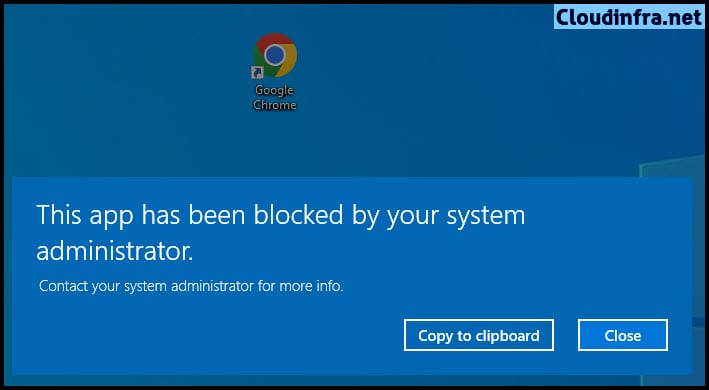
Launch the EXE app blocked by the Applocker rule, you should see the below message:
This app has been blocked by your system administrator
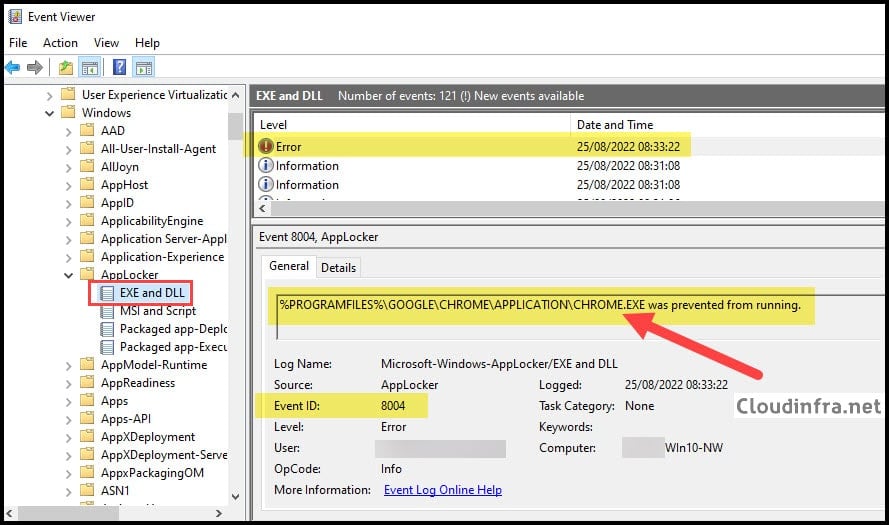
Applocker Event ID 8004
You can locate AppLocker-related events in the Event Viewer by following the below steps:
- Go to Start > Search for Event Viewer.
- Expand Application and Services logs > Microsoft > Windows.
- Find AppLocker folder.
- Click on EXE and DLL.
- You will find that Event ID 8004 is generated when an application is prevented from running. This confirms that the policy we applied from Intune is working fine.
FAQs
1. How to Delete Applocker Policy?
Once you have exported AppLocker rules into an XML file, it is unnecessary to keep those rules in place on the test device from where you exported the file. You can delete those rules if they are no longer required.
- Press Windows + R to open Run Dialog box.
- Type secpol.msc and Press Enter.
- Expand Application Control Policies.
- Right-click on AppLocker and select Clear Policy.
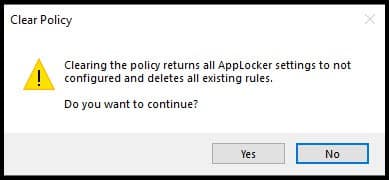
- When you click Clear Policy, a warning popup will appear to confirm whether you want to delete all the rules created on your device. Click on Yes.
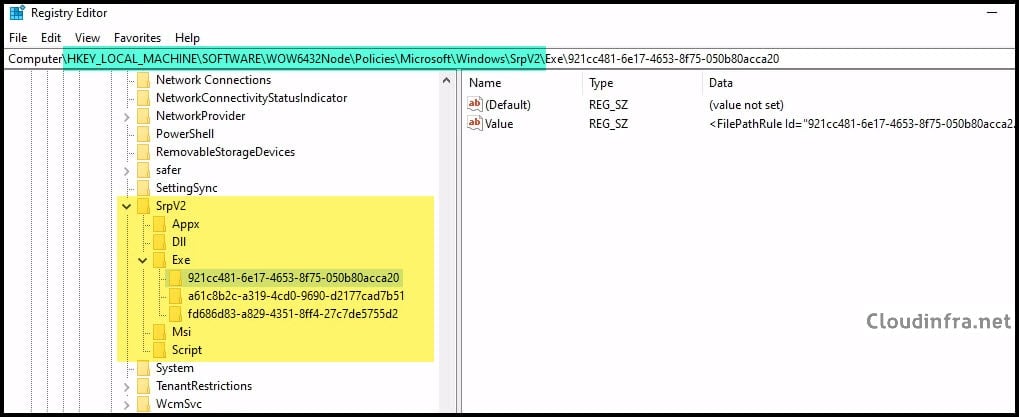
2. Where are AppLocker rules stored in the registry?
You can locate AppLocker rules at the registry location:
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\SrpV2
- HKEY_LOCAL_MACHINE\SOFTWARE\WOW6432Node\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\SrpV2
3. Applocker Rules Storage Location on End User Device
You can locate Applocker rules on the target device at C:\Windows\System32\AppLocker\MDM location.
hi, does it work even if the file name is changed?
No, it won’t. If you want the rule to remain effective even if the file name is changed, you’ll need to adjust the slider to generalize at the Product Name level rather than the File name level. Hope that clarifies things.
I have tried to change file name from FortiClient.exe to FortiClientxxx.exe and it still works. FortiClient application is blocked. any idea?
You must include the FortiTray.exe executable.
Thank you for you article. It is very helpful
quick question.
I need to block 3 applications for all users, except one application for a specific group.
Applications 1 and 2 are blocked for the “All Users” group.
Application 3 is blocked for All Users but excluded for a specific group.
If I now create two configurations in Intune.
One configuration where the Applocker block application 1 and 2 -> All Users
Second configuration in which Applocker block application 3 ->All Users / exclude one group
but now I get an policy conflict with this two configurations, because both are leading to the same OMA URL: ./Vendor/MSFT/AppLocker/ApplicationLaunchRestrictions/apps/EXE/Policy
Hey fabs, Could you group these into one single configuration. Block Application 3 for a specific group + Application 1 and 2 in the same configuration? Why do you need two EXE Policies?
Hello, how can I enable APPLocker if I have 1000 users? (There is no on-premise AD.)
Add users to Entra security group and target Applocker policies to the group. Test the policy on few users first, once its working fine. Deploy it on 1000 users.
Great post! The step-by-step approach made it easy to follow along. I especially appreciated the tips on troubleshooting common issues. Looking forward to implementing Applocker in our organization using these guidelines!
Great doc.
Question: i need to block mshta.exe via intune, the steps are the same as you done with chrome?
Hi @Jatin
Thanks for the post is a great one.
I wanted to block chrome also. It worked, but what I have found is that on applying the policy in Intune via OMA-URI and the policy is applied there are other apps that are being blocked there.
Like all shortcouts on taskbar or a Remote Desktop App from Windows itself.