In this post, I will show you how to manage Windows driver updates with Intune. When you create a driver updates policy in Intune, you get the ability to review, approve, decline or pause the installation of drivers, and assign those rules to device groups. Based on the policy you configure in Intune, Windows Update for client policies only offers approved and applicable driver updates to Windows devices.
Each device runs its normal Windows Update scan, sees only the latest approved driver compatible with its hardware, and installs it according to the update ring and driver-update policy settings (for example, driver install is allowed/blocked, deferral settings, active hours, and maintenance windows etc.).
Windows update for client sends the diagnostic data back to Intune so you can track deployment status, ensure compliance and generate reports. For a complete overview and architecture, refer to the Microsoft docs page: Learn about Windows Driver updates policy for Windows devices in Intune – Microsoft Intune | Microsoft Learn
Contents
Prerequisites for Windows Driver Update Management
- Licensing: Microsoft Intune Plan 1 and Entra ID free or greater plan plus any of the below licenses:
- Windows Enterprise E3 or E5 (included in Microsoft 365 F3, E3, or E5)
- Windows Education A3 or A5 (included in Microsoft 365 A3 or A5)
- Windows Virtual Desktop Access E3 or E5
- Microsoft 365 Business Premium
- Device state:
- Devices must be enrolled in Intune.
- Entra joined or Entra hybrid joined.
- Supported version of Windows 11 OS (Supported Editions are: Pro, Enterprise, Education, Pro for Workstations). Home edition and Windows Enterprise LTSC are not supported.
- Telemetry switched on and set to at least Required (Basic) level.
- Microsoft Account Sign-In Assistant (wlidsvc) must not be disabled or blocked.
- Update ring policy: Your update ring policy must not block the driver updates.
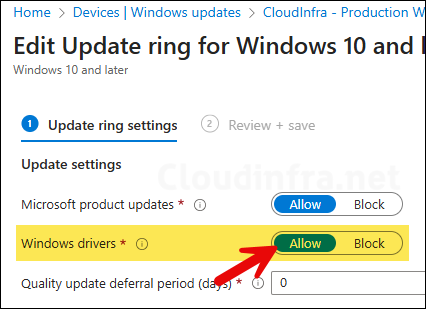
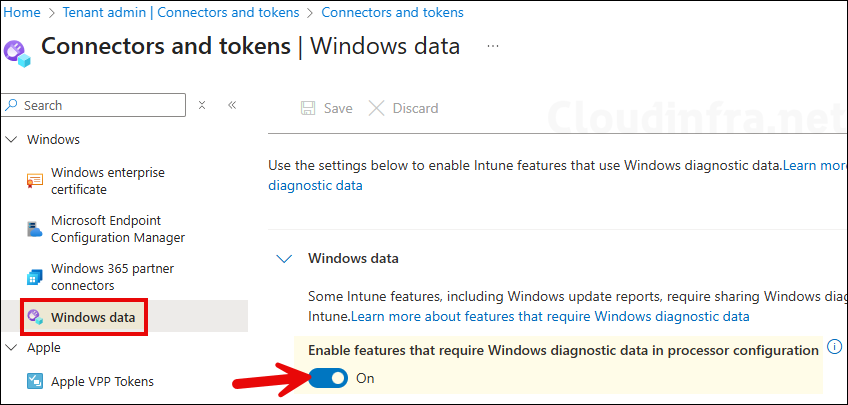
- Ensure that the setting Enable features that require Windows diagnostic data in processor configuration toggle is set to On. This is required for Windows driver updates reporting in Intune.
- Ensure that the devices have access to the required Network endpoints.
Important Points
Before we go through the steps to create and assign a driver update policy in Intune, there are a few important points you should know about this feature.
- As of now, driver updates are not supported during Autopilot.
- Roll back of a driver update is not supported.
- Quality Update deadline and grace period settings apply to driver updates.
- Deferral period set for Quality Updates in the Update Rings policy does not apply to drivers that are approved using the Driver Update Policy. Use the deferral settings in driver update policy.
- BIOS and firmware updates published to Windows Update (WU) does not require BIOS/UEFI to be unlocked.
- Microsoft does not recommend assigning multiple driver update policies to a single device. Add a device to single driver update policy only.
- User experience settings from Update ring policy, such as automatic update behavior, active hours, notifications, and so on, are applied for driver updates as well.
- It’s not mandatory to enable and use Windows AutoPatch for creating driver management. You can create driver update policy with Update ring policy created without using AutoPatch.
Create Phased Deployment Groups
Driver updates can sometimes cause issues on Windows devices, so it’s best to test them on test devices before rolling them out to business users. For a phased deployment approach, you can create multiple deployment rings and assign them to their respective Entra groups.
For example, I’ll create the deployment rings and Entra groups as shown in the below table. I’ll use the Auto-approve driver updates approach, as it’s simpler and requires less administrative effort than manual approval method. As we are using a number of deployment rings for a phased deployment, If there are any issues, you can detect them early in the initial deployment rings and easily pause the driver update before it is distributed to other devices in later deployment rings. Refer to the next section for understanding the difference between automatic and manual approach.
| Deployment Ring | Entra Group | Deferral |
|---|---|---|
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Test | Test Devices Group | 0 |
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Pilot | Pilot Devices Group | 5 |
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Early Adopters | Early Adopters Devices Group | 10 |
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Prod 01 | Prod01 Devices Group | 15 |
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Prod 02 | Prod02 Devices Group | 20 |
| Driver Updates (Auto Approve) – Prod All | Prod All Devices Group | 30 |
Creating Driver Update Profile in Intune
Now that we understand the prerequisites and gone through important points about the Windows driver update management in Intune, we can start with the creation of a driver update policy.
- Sign in to the Intune admin center portal and navigate to Devices > Windows updates > Driver updates. Click on + Create profile.
- On the Basics tab, provide a name and description of the profile and Click Next.
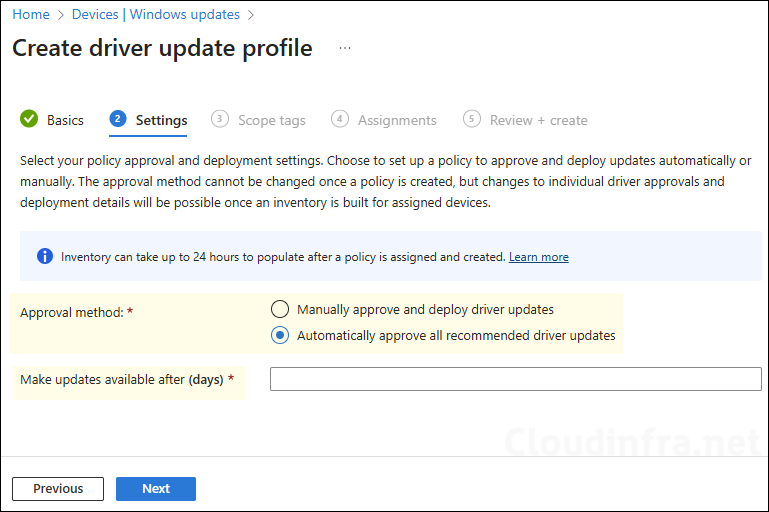
- On the Settings tab, configure the approval method and Make updates available after (days) options.
- Manually approve and deploy driver updates: When you select this option, you must manually approve each new driver update before it can be deployed to devices. When a driver is added to the policy, its status appears as Need review. At the time of approving a manual update, you can also select a date when you want this update to be installed on the applicable devices.
- Automatically approve all recommended driver updates: When you choose this option, all new recommended driver updates are automatically approved and deployed. No manual action is required. You will also have the option to configure the Make updates available after (days) setting to control when updates become available to devices.
- Make updates available after (days): This is a deferral period that delays the deployment and installation of a recommended driver update that has been marked as Approved. You can set a value between 0 and 30 days. The timer starts from the day the update was added to the policy, not from the date it was published by the OEM to Windows Update.
- Scope tags (optional): A scope tag in Intune is an RBAC label you add to resources (policies, apps, devices) to limit which admins can see and manage them. For more Information, read: How to use Scope tags in Intune.
- Assignments: Assign the profile to Entra security groups that contain the Windows devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + create: Review the deployment summary and click Create.
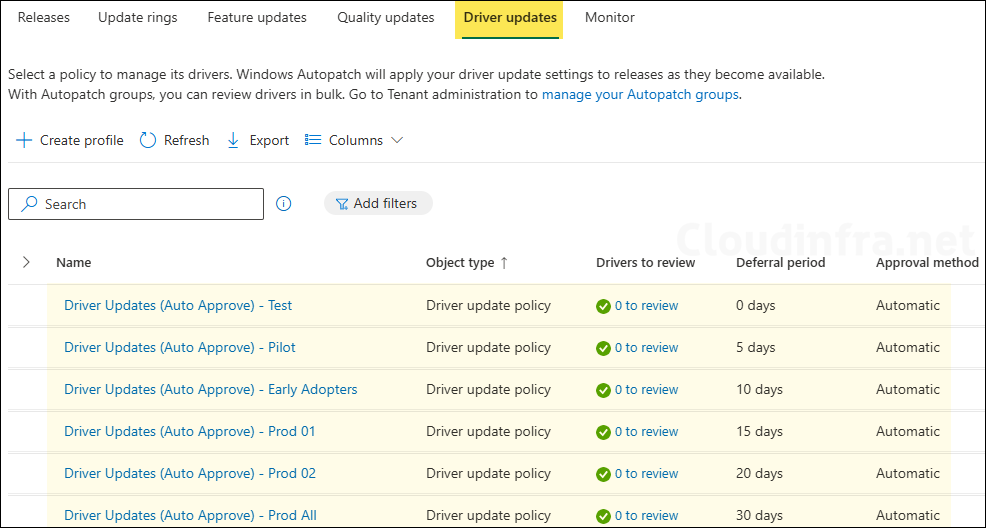
Following the phased deployment approach for deploying driver updates to all Intune-managed Windows devices, I created the deployment rings and assigned them to their respective Entra groups. The deferral period for each ring has been configured as shown in the screenshot below.
Administrator Experience
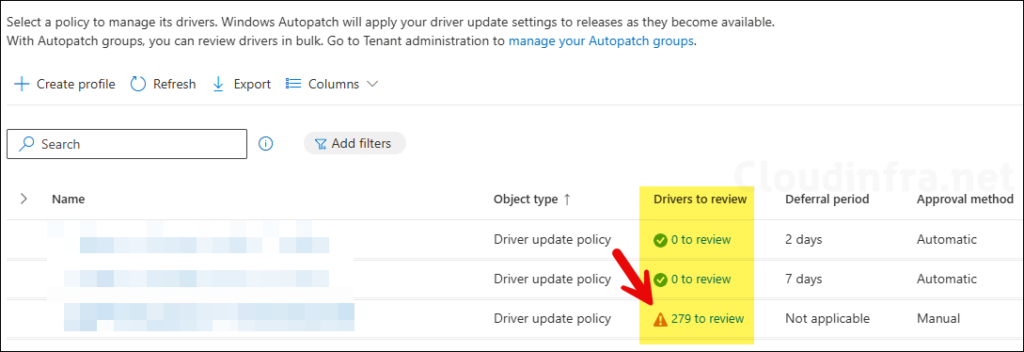
Once the Windows Update scan is complete and the driver data is updated in the Intune portal, the administrator will be able to review it. Under the Drivers to review column, click the link showing X to review, where X represents the number of drivers pending administrator approval.
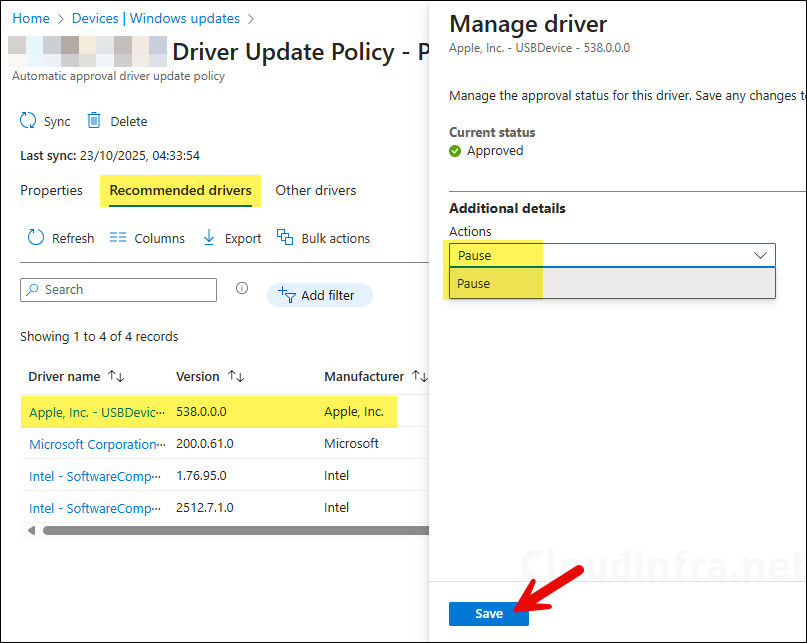
If it is an automatic approval driver policy, all drivers listed under the Recommended drivers tab will be automatically approved. You can click on any driver and choose Pause if you do not want it to be installed on the target devices.
If it is a manual approval policy, the drivers listed under the Recommended drivers tab will not be automatically approved. Click on the driver you want to manage, then select either Approve or Decline.
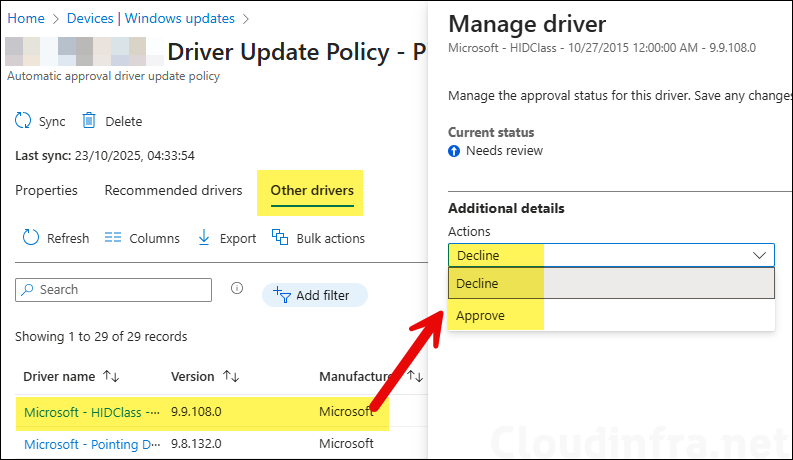
The drivers listed in the Other drivers table will also not be automatically approved. You can click on any driver you want to manage on the target devices and select either Approve or Decline.
End User Experience
After you create driver update policies in Intune and devices are enrolled for management, Windows update must wait for each device to perform its daily scan for updates. It may take up to 24 hours for devices to check in. Intune will process the scan results and provide the available and applicable driver updates to the device.
You can check the driver updates on the device by going to the Settings app > Windows update. When the driver updates are offered and installed, you will be able to check the status from Windows update page. As the scan is still pending and there are currently no drivers approved or available for this device, below screenshot does not show any drivers in the list of updates.
Manage Driver Policies using Microsoft Graph
You can also manage the driver policies using Microsoft graph queries. I will show you an example of couple of graph queries, for more information and other actions that you can perform using Microsoft graph with respect to the management of driver policies in Intune, refer to Microsoft documentation link: windowsDriverUpdateProfile resource type – Microsoft Graph beta | Microsoft Learn.
1. WindowsDriverUpdateProfiles
This is the Intune resource that represents the Driver updates for Windows 10 and later policy you see in the Intune portal. Use this to script day-to-day driver management in Intune: create profiles, assign to groups, approve or pause drivers, and read device status. MS docs reference: List windowsDriverUpdateProfiles – Microsoft Graph beta | Microsoft Learn
You will need the necessary Microsoft Graph permissions and admin consent before running below commands. If you are using Graph Explorer to run these commands, they will fail until you grant consent for the required permissions needed to perform the actions specified in the query.
Useful actions for this resource
/driverInventorieslist drivers known to the profile, including approval status./deviceStatusessee per-device state and timestamps for the profile./assignassign the profile to groups./executeActionapprove, pause, or decline specific driver IDs (bulk).- Update profile properties such as approval type.
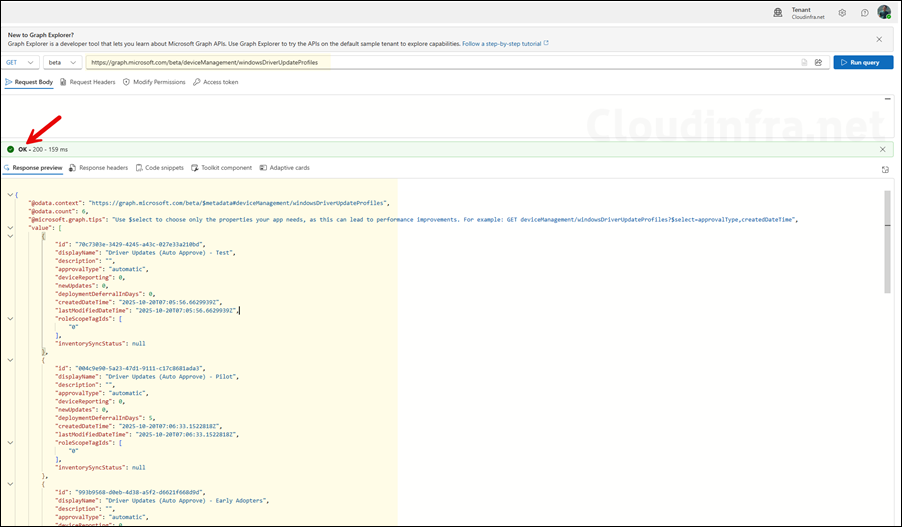
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles
PATCH https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{id}
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{id}/driverInventories
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{id}/deviceStatuses
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{id}/assign
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{id}/executeAction- Open the Microsoft Graph explorer and run below query:
https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles Without the right permissions, you will get the error: Application is not authorized to perform this operation. Application must have one of the following scopes: DeviceManagementConfiguration.Read.All and DeviceManagementConfiguration.ReadWrite.All.
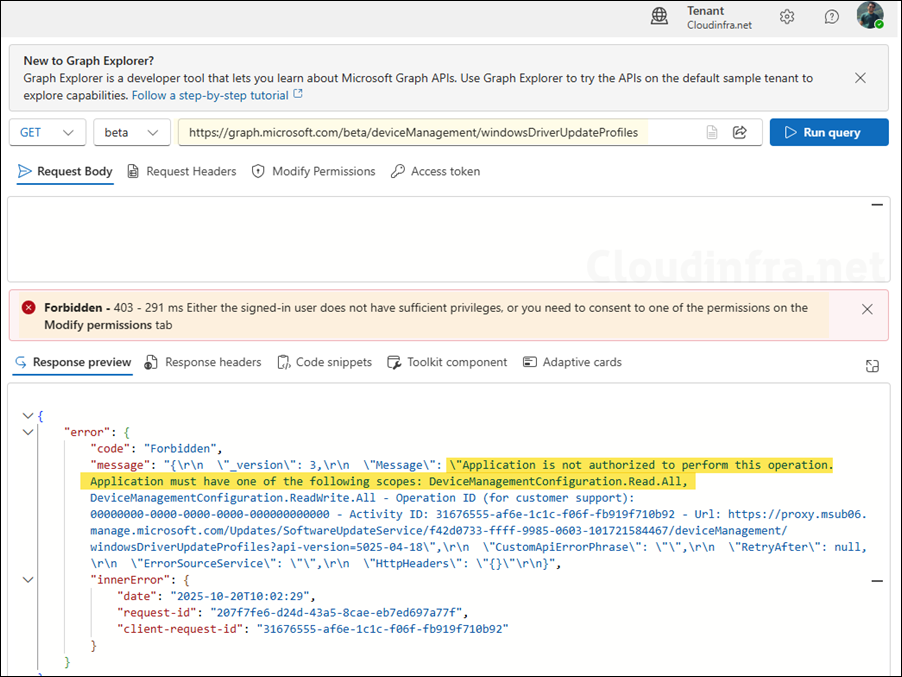
Click on Modify permissions tab and then Click Consent and sign in with your credentials.
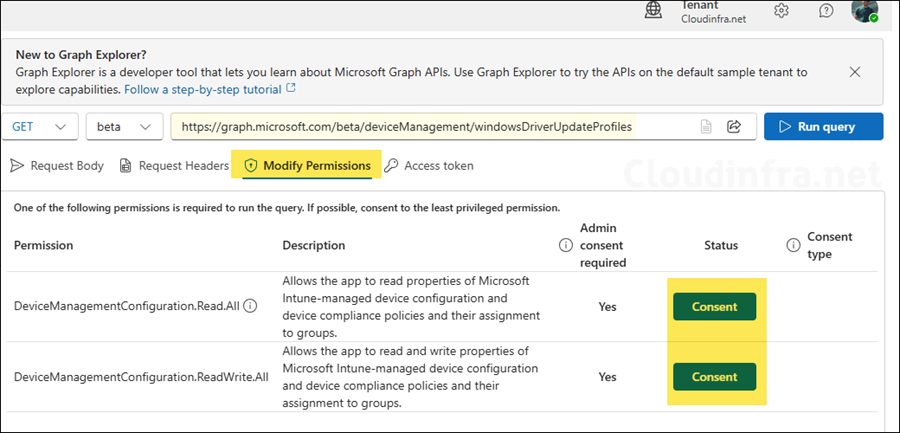
After obtaining the required permissions to run the Graph query, you’ll be able to view the details of all driver update policies created in the Intune portal.
https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles
{
"@odata.context": "https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/$metadata#deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles",
"@odata.count": 6,
"@microsoft.graph.tips": "Use $select to choose only the properties your app needs, as this can lead to performance improvements. For example: GET deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles?$select=approvalType,createdDateTime",
"value": [
{
"id": "70c7303e-3429-4245-a43c-027e33a210bd",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Test",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 0,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:05:56.6629939Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:05:56.6629939Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
},
{
"id": "004c9e90-5a23-47d1-9111-c17c8681ada3",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Pilot",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 5,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:06:33.1522818Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:06:33.1522818Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
},
{
"id": "993b9568-d0eb-4d38-a5f2-d6621f668d9d",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Early Adopters",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 10,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:02.9034299Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:02.9034299Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
},
{
"id": "79678786-9bc5-4c84-ad12-daee5c609948",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Prod 01",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 15,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:32.887368Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:32.887368Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
},
{
"id": "cfe4f75c-79e7-4c49-bf65-4dba41e2ca94",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Prod 02",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 20,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:50.1037965Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:07:50.1037965Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
},
{
"id": "2622964d-e536-45d9-b203-4786866ac09a",
"displayName": "Driver Updates (Auto Approve) - Prod All",
"description": "",
"approvalType": "automatic",
"deviceReporting": 0,
"newUpdates": 0,
"deploymentDeferralInDays": 30,
"createdDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:08:10.9011635Z",
"lastModifiedDateTime": "2025-10-20T07:08:10.9011635Z",
"roleScopeTagIds": [
"0"
],
"inventorySyncStatus": null
}
]
}
Approve a set of drivers with availabiltity date
You can approve a set of drivers by sending a POST command using the deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles namespace. Replace the {profileId} and {driver-guid} values in the code before executing below graph command.
Approve a set of drivers
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/deviceManagement/windowsDriverUpdateProfiles/{profileId}/executeAction
Content-Type: application/json
{
"actionName": "approve",
"parameters": {
"driverIds": ["{driver-guid-1}","{driver-guid-2}"],
"deploymentDate": "2025-10-25T09:00:00Z"
}
}2. /updates/updatePolicies
Service-side update policy objects in the Windows Update deployment service. Use when you are automating Windows Update deployments at the service layer (feature updates, quality updates, and drivers via the Autopatch catalog), not the Intune driver policy UI. You can list, create, and update these policy objects. (Windows Update Deployment Service).
GET https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/admin/windows/updates/updatePolicies // list
POST https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/admin/windows/updates/updatePolicies // create
PATCH https://graph.microsoft.com/beta/admin/windows/updates/updatePolicies/{id} // updateThese policies are part of the Windows Updates (deployment service) namespace and work with related resources like deployments, updatableAssets, and catalog entries. This is useful for building your own automation around the Windows Updates deployment service, including grouping devices, targeting deployments, and working with the Microsoft Update catalog.
Conclusion
This post is a quick-start guide for implementing and managing Windows driver update policies through Intune. If your organization has the required licenses, I recommend exploring this feature for better control over driver update management. Using phased deployment rings helps minimize the risk of widespread issues by detecting problems in the early stages, allowing IT administrators to pause deployments for faulty drivers before they reach other devices.