In this blog post, we will demonstrate the steps to deploy shell scripts on macOS using Intune admin center. Shell script contains a list of UNIX commands that can be executed on the target device to achieve the desired result.
- Shell Script Use Cases
- You can create a Shell script to set desktop wallpaper on a macOS device.
- Create a local admin account on macOS using a Shell script.
Best practice for deploying shell scripts on macOS is to first test the script on a test device first. This will reduce the failure rate and saves a lot of time in deployment process. One of the advantages of deploying shell scripts via Intune is that you can schedule script deployment and set a script frequency.
Contents
Prerequisites
- Devices with macOS 11.0 and later.
- macOS Devices must be enrolled and managed by Intune.
- Target macOS devices must be connected to the Internet without any Proxy.
- Shell scripts begin with #! and must be in a valid location, such as
#!/bin/shor#!/usr/bin/env zsh. - Command-line interpreters for the applicable shells are installed.
Pre-Deployment Points for macOS Shell Scripts
Before you start your deployment of Shell scripts using Intune, There are a few important points to consider. You should review it to understand how the shell script deployment will work.
- Shell scripts requires Microsoft Intune management Extension (IME) which would be automatically and silently installed on the device that are assigned at least one shell script from Intune admin center.
- Shell scripts run in parallel on devices as separate processes.
- Shell scripts run as the signed-in user will run for all currently signed-in user accounts on the device at the time of the run.
- An end user must sign in to the device to execute scripts running as a signed-in user.
- Root user privileges are required if the script requires making changes that a standard user account cannot.
- Shell scripts will attempt to run more frequently than the chosen script frequency for certain conditions. Examples include 1) if the disk is full, 2) if the storage location is tampered with, 3) if the local cache is deleted, or 4) if the Mac device restarts.
- Shell scripts running for over 60 minutes are stopped and reported as failed.
Shell Script Preparation
You need to prepare and test a Shell script to deploy on Intune-managed macOS devices. I am using below example Shell script for demonstration, which will create a local administrator account on Mac devices. You can use the steps in this post to deploy any Shell script on Mac.
createLocalAdmin.sh
!/bin/sh
accountname=cloudinfraadmin
password="C0mputer@2020"
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname UserShell /bin/bash
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname RealName "CloudInfra Admin Account"
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname UniqueID "2001"
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname PrimaryGroupID 20
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname NFSHomeDirectory /Users/$accountname
dscl . -passwd /Users/$accountname $password
dscl . -create /Users/$accountname hint "computer"
dscl . -append /Groups/admin GroupMembership $accountnameCreate a Shell Script Deployment
Now that the Shell script is ready and manual testing is successful, we will create a Shell script deployment on the Intune admin center.
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > macOS >Shell scripts.
- Click on + Add to start creating the deployment.
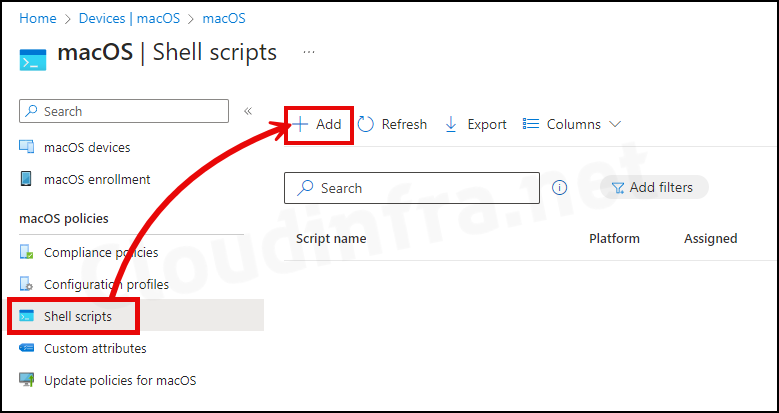
- Basics Tab: Enter the Name and Description and click on Next.
- Script Settings
- Run script as signed-in user: Select No to run the script using root-level privileges, similar to running the script as an administrator. The default value of this setting is Yes; change it to No. If you have a shell script that you want to execute in User context, keep the default value of Yes.
- Hide script notifications on devices: Users will get a Script notification by default. Select Hide to hide script notifications.
- Script frequency: You can configure how often you want the script to execute on the device. By default, it will be executed only once.
- Max number of times to retry if script fails: Select how many times you want the script to be re-executed on failure. When you choose Not Configured, a retry of script execution on failure will not occur.
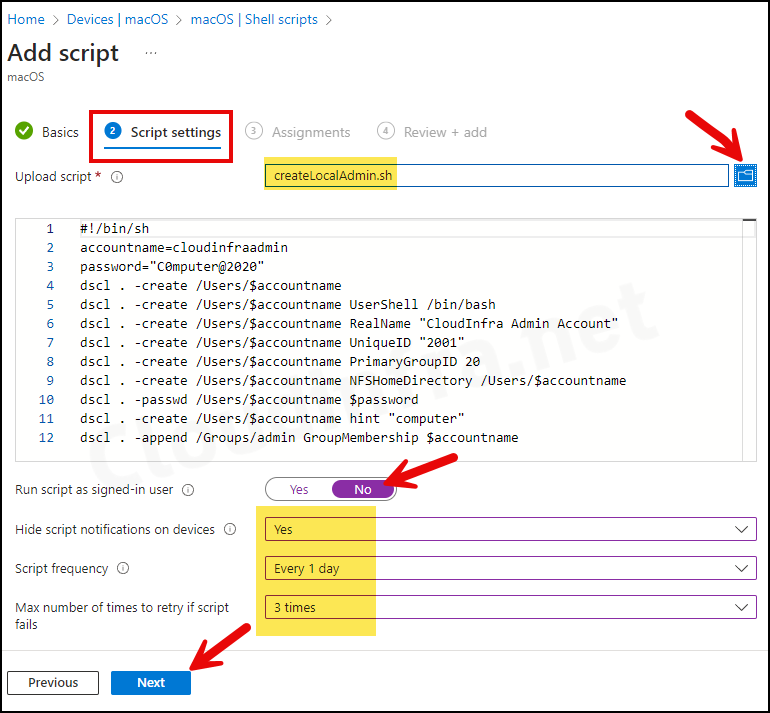
- Assignments: Assign the policy to Entra security groups that contain the target users or devices. As a best practice, pilot with a small set first; once validated, roll it out more broadly. For guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + add: Review the Summary of your deployment and Click on the Add.
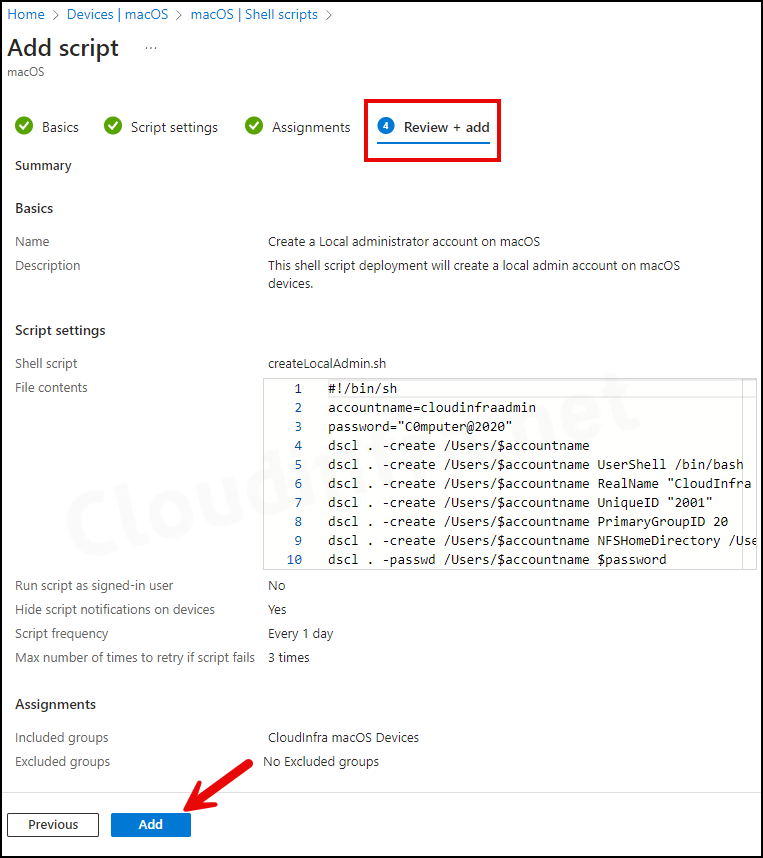
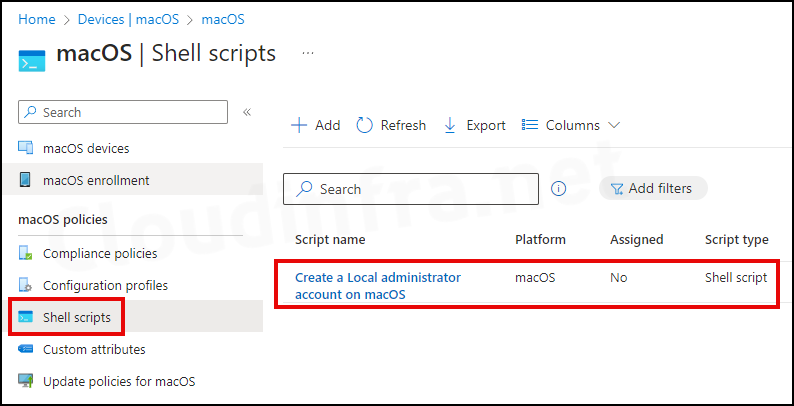
MacOS Shell script deployment has been created in the Intune admin center. The deployment is from Intune admin center > Devices > macOS > Shell scripts.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
Monitor Deployment Progress
To monitor app deployment, access the Intune admin center. Navigate to Devices > macOS > Shell scripts. Click on a shell script to check its status, then go to the Overview page to view the shell script deployment status.
To check the deployment status on a per-device or per-user basis, select Device status or User status under the Monitor section.
macOS Shell Script Deployment Status
After creating a Shell script deployment on Intune, target it to macOS devices/users. The script may take a few hours to execute, and the status will be reported back to Intune. Below is the status reported to Intune depending on whether the Script execution was successful or failed.
| Script Status | About the Result |
|---|---|
| Success | Shell script execution was successful. Script returned Zero (0) exit code. |
| Failed | Shell script execution was not successful. Script returned a Non-Zero exit code. |
| No Status | If the device is offline, No status can be reported to Intune until the device is back Online. Therefore, in that case, Intune will show as No Status. |
Troubleshooting
If you encounter issues deploying the shell script, use the troubleshooting steps below to identify the root cause.
Shell Scripts Not Running on Target macOS Devices
Even if you have successfully tested the shell script manually before creating the deployment in the Intune admin center, it may still fail to run on some target macOS devices. Below are a few reasons the shell script might fail to execute:
- If you recently created the Script deployment, you may need to wait for the Intune device check-in process to complete. For more information about the Intune device check-in process on Mac devices, refer to the article: Force Intune Sync on macOS devices. The default device check-in happens every 8 hours.
- Ensure the target device is online and connected to the Internet for successful MDM agent check-in. If the device is online, you can ask the user to open the Company Portal app on their device and Initiate Device check-in once.
- Ensure that the Intune agent is installed on the target Mac device. Intune agent is installed at the location /Library/Intune/Microsoft Intune Agent.app. Check if Microsoft Intune agent.app exists.
- Review Intune logs on macOS devices. To collect and investigate the logs, refer to the step-by-step guide on log collection: How to Collect Intune Logs from macOS Devices.
- If there are issues with the Intune agent, it typically recovers within 24 hours. Allow time for it to move from an unhealthy to a healthy state. If problems persist after 24 hours, raise a support ticket with Microsoft.