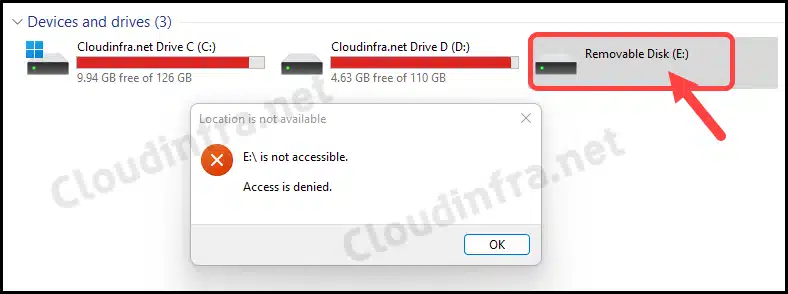
In this blog post, I will show you the steps to block USB drives on Windows using Intune remediations. There is always a security risk when USB storage drive access is allowed on corporate devices. Users can download sensitive data on external drives, which, if misused, could affect the organization’s reputation.
Blocking removable storage devices on company-owned devices is essential for preventing potential security breaches. By doing so, you can ensure that confidential information is not saved or copied to personal storage devices, thereby safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining a secure working environment.
I will use Intune device remediations to block USB drives on Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices. You can also block USB drives using a Device restriction template or Attack surface reduction policy. For more Information, refer to the guide: 3 Ways to Block USB Drives using Intune.
Remediations requires users of the devices to have one of the following licenses. If you are not meeting the license criteria, then you can simply deploy Remediation_Script_Block_USB.ps1 script via Intune admin center > Devices > Scripts and Remediations > Platform scripts option. For more information, refer to the blog post: How to deploy a Powershell script using Intune.
Source: Microsoft
- Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 or E5 (included in Microsoft 365 F3, E3, or E5)
- Windows 10/11 Education A3 or A5 (included in Microsoft 365 A3 or A5)
- Windows 10/11 Virtual Desktop Access (VDA) per user
After several iterations and testing, I have successfully created the scripts that works fine on both Windows 10 and Windows 11 devices. The script effectively blocks USB access by creating a registry key named RemovableStorageDevices. Under this registry key, I will create a registry entry called Deny_All and set its value to 1, preventing access to removable storage devices.
For checking if the registry key and value exists, I have referred to and modified the Powershell script from the blog post: Powershell to test If registry key and value exist.
Note
Contents
Prepare PowerShell scripts
We will require two PowerShell scripts, First one for detecting if RemovableStorageDevices registry key and Deny_All registry entry with value of 1 exists or not. If it does not exist, a remediation script will be triggered to fix it and ensuring that the USB drive remain blocked. You can also download these PowerShell script from my GitHub repository: Block USB Drives Remediation Scripts.
Detection_Script_Block_USB.ps1
<#
.DESCRIPTION
This detection script will check if RemovableStorageDevices reg key
is existing and Deny_All is set to 1
Author: Jatin Makhija
Website: Copyright - Cloudinfra.net
Version: 1.0.0
#>
#registry key path
$regPath = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\RemovableStorageDevices"
#Provide registry entry display name
$valueName = "Deny_All"
#Provide registry entry expected value
$requiredValue = "1"
$regkeyexists = Test-Path -Path $regPath
if ($regkeyexists) {
#Check if registry entry named Status exists
$regentryexists = Get-ItemProperty -Path $regpath -Name $valueName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if ($regentryexists) {
#If registry entry named Deny_All exists, then fetch its value
$currentValue = Get-ItemProperty -Path $regpath | Select-Object -ExpandProperty $valueName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
#Match Status registry entry value with requried value
if ($currentValue -eq $requiredvalue) {
Write-Host "Reg value exists and matching the required value."
Exit 0
} else {
Write-Host "Reg value exists, but does not match the required value."
Write-Host "Current value: $currentValue"
Write-Host "Required value: $requiredValue"
Exit 1
}
}
else {
Write-Host "Registry value does not exist."
Exit 1
}
}
else {
Write-Host "Registry key does not exist."
Exit 1
}
- Below, the Remediation PowerShell script will check the existence of the RemovableStorageDevices registry key and whether Deny_All with a value of 1 exists. If any conditions are false, the registry item will be created or updated accordingly.
Note
- Script will create a registry key RemovableStorageDevices if it does not exist.
- Script will create a registry entry Deny_All with value 1, Only when it does not exist.
- Script will update registry entry Deny_All if its set to any value other than 1.
Remediation_Script_Block_USB.ps1
<#
.DESCRIPTION
This remediation script will check if RemovableStorageDevices reg key
is existing and Deny_All is set to 1. If not then it will create it
Author: Jatin Makhija
Website: Copyright - cloudinfra.net
Version: 1.0.0
#>
#Registry key path
$regPath = "HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\RemovableStorageDevices"
#Provide registry entry display name
$valueName = "Deny_All"
#Provide registry entry expected value
$requiredValue = "1"
$type = "DWORD"
$regkeyexists = Test-Path -Path $regPath
If (!$regkeyexists)
{
try{
New-Item -Path $regPath -Force | out-null
Set-ItemProperty -Path $regPath -Name $valuename -Value $requiredValue -Type $type
Write-Output "Registry Key and value created"
Exit 0
}
Catch {
$errMsg = $_.Exception.Message
Write-Error $errMsg
Exit 1
}
}
Else
{
Write-Output "Reg Key exists. Checking for registry entry"
$regentryexists = Get-ItemProperty -Path $regpath -Name $valueName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
If ($regentryexists)
{
Write-Output "Reg Entry Exists. Checking for its value"
$currentValue = Get-ItemProperty -Path $regpath | Select-Object -ExpandProperty $valueName -ErrorAction SilentlyContinue
if ($currentValue -eq $requiredvalue)
{
Write-Output "Reg entry with value already Exists.No action required"
Exit 0
}
Else {
Set-ItemProperty -Path $regPath -Name $valuename -Value $requiredValue -Type $type
Exit 0
}
}
Else {
Set-ItemProperty -Path $regPath -Name $valuename -Value $requiredValue -Type $type
Exit 0
}
}
Create a Script Package
Now that we have prepared the PowerShell scripts, create a device remediations package on Intune admin center to deploy the scripts and create necessary registry keys and values to block USB drives.
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > Scripts and remediations.
- Click on + Create under the Remediations tab.
- Basics Tab – Provide the Name and Description of the package.
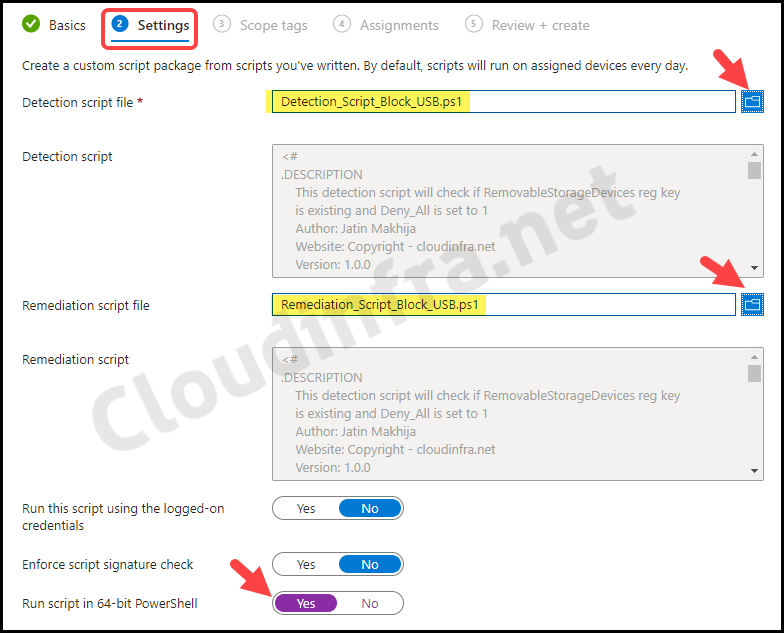
- Settings Tab – Browse to detection and remediation scripts and configure below settings.
- Detection script file – Browse to the Detection script Detection_Script_Block_USB.ps1
- Remediation script file – Browse to Remediation script file Remediation_Script_Block_USB.ps1
- Run this script using the logged-on credentials – No
- Enforce script signature check – No
- Run script in 64-bit Powershell – Yes
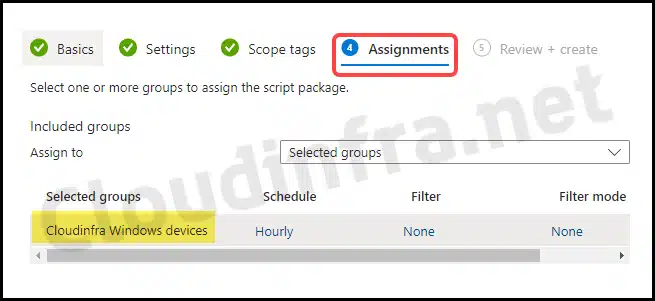
- Assignments: Click on Add group to add an Entra security group containing users or devices. You can also select the Schedule to run this script package. You have three options: Once, hourly, or Daily. For further guidance on assignment strategy, see Intune assignments: User groups vs. Device groups.
- Review + create: Review the deployment and click on Create.
Sync Intune Policies
The device check-in process might not begin immediately. If you’re testing this policy on a test device, you can manually kickstart Intune sync from the device itself or remotely through the Intune admin center.
Alternatively, you can use PowerShell to force the Intune sync on Windows devices. Restarting the device is another way to trigger the Intune device check-in process.
Monitor the script package
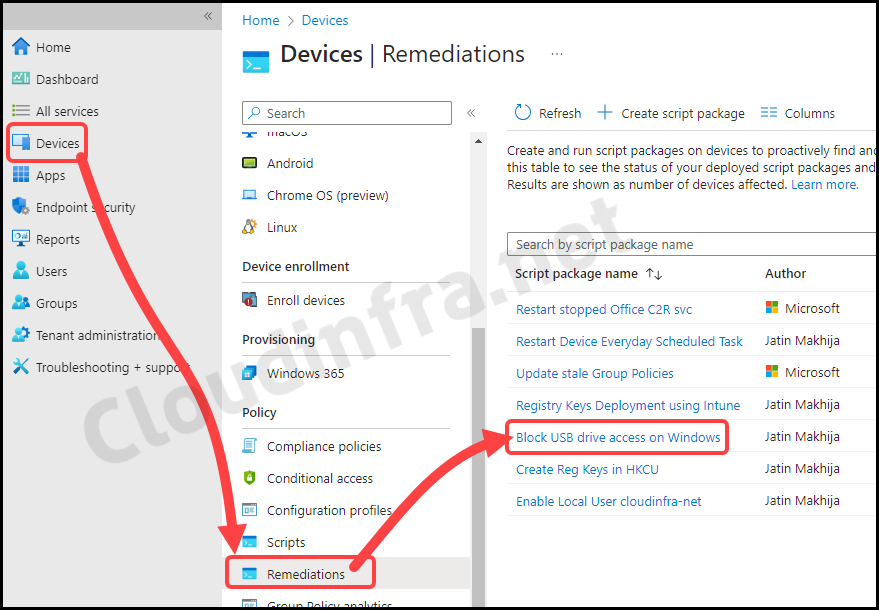
To monitor the progress of a script package deployed via Intune, follow the below steps:
- Sign in to the Intune admin center > Devices > Scripts and remediations.
- Click on the Remediation script package you want to monitor: for example, Block USB drive access on Windows.
- Go to the Overview to find the deployment status of the script package.
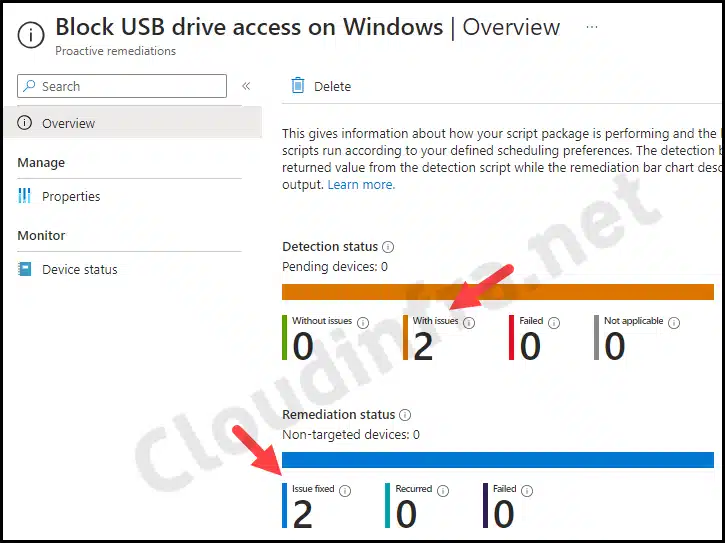
End User Experience
After completing the deployment, registry entries will be created according to the remediation script. Let’s confirm it from one of the target device:
- Press the Win + R keys to open the Run dialog box
- Navigate to HKLM:\SOFTWARE\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\ to confirm if the RemovableStorageDevices registry key has been created with a Deny_All registry entry with a value of 1.
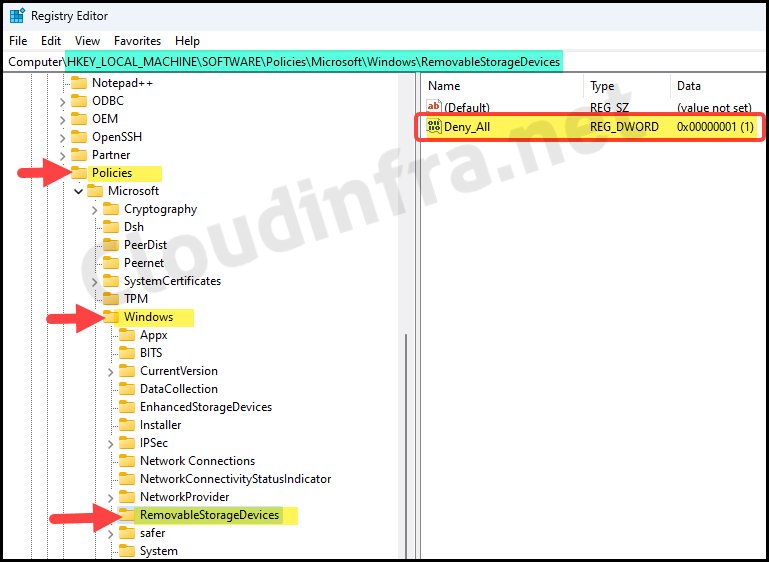
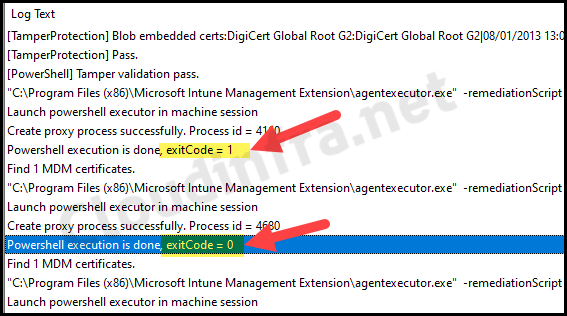
Find Intune Device Remediation Script Logs on the Device
You can find Intune device remediation script logs in IntuneManagementExtension.log file which can be located at C:\ProgramData\Microsoft\IntuneManagementExtension\Logs path.
Conclusion
In this blog post, we have used Intune device remediations method for blocking USB drives on Windows 10/11 devices. However, there are other ways to block USB drives like using Device restrictions template or Attack surface reduction policy available on Intune admin center. You can refer to my other blog post where I have covered both these scenarios for blocking USB drives: 3 Ways to block USB drives using Intune.
Hello Jatin,
Apparently specific Windows licenses are required to use the Intune Remediations options.
https://learn.microsoft.com/en-us/intune/intune-service/fundamentals/remediations
Licensing
Remediations requires users of the devices to have one of the following licenses:
Windows 10/11 Enterprise E3 or E5 (included in Microsoft 365 F3, E3, or E5)
Windows 10/11 Education A3 or A5 (included in Microsoft 365 A3 or A5)
Windows 10/11 Virtual Desktop Access (VDA) per user
Is there are an alternative way to deploy these two scripts?
Hi Mansa,
You can create a standalone PowerShell script and deploy it using the Intune admin center by navigating to Devices > Scripts. You can use this blog post for reference: https://cloudinfra.net/how-to-deploy-a-powershell-script-using-intune/
Hi Jatin, thanks for this.
Intune failed at this task _miserably_ (early 2024) but your scripts work really well, thank you!
Wondering if you’ve come up with a way to allow certain removable storage devices while still preventing anything not on that list?
I’ve found the key, Software\Policies\Microsoft\Windows\EnhancedStorageDevices\ApprovedEnStorDevices\List
but adding Hardware or Device ID’s to this has had exactly zero effect. Maybe I’m approaching it the wrong way?
Thanks for your time, any suggestions you have would be most appreciated.
Sean