In this blog post, we will cover the fix for the issues we experience when Windows PowerShell Launching and Closing abruptly. Let’s start with Issue description and then proceed to solutions.
Contents
Issue Description
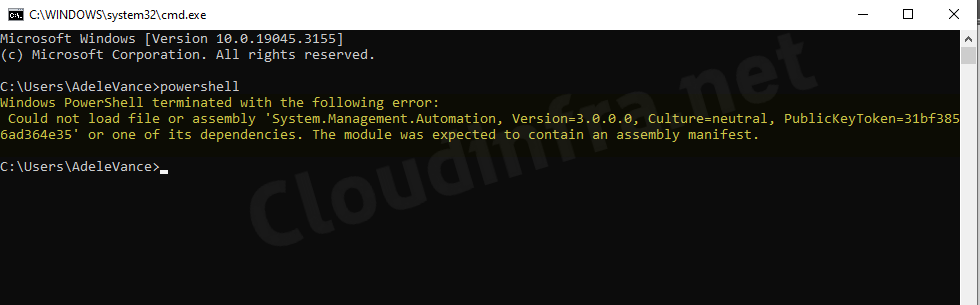
When attempting to launch PowerShell on a Windows 10/11 device, I encountered a flashing PowerShell window that closed automatically. PowerShell ISE (Integrated Scripting Environment) also fails to launch on the device.
Even after multiple restarts of the device, the issue remains unresolved. Attempts to launch PowerShell through the Windows Command Prompt have also resulted in the following error:
Windows PowerShell terminated with the following error: Could not load file or assembly ‘System.Management.Automation, Version=3.0.0.0, Culture=neutral, PublicKeyToken=31bf3856ad364e35’ or one of its dependencies. The module was expected to contain an assembly manifest.
Root Cause
If you encounter this error, the issue may stem from a corrupted system file or module called System.Management.Automation.dll. This file is typically located at C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\System.Management.Automation\v4.0_3.0.0.0__31bf3856ad364e35.
Solution
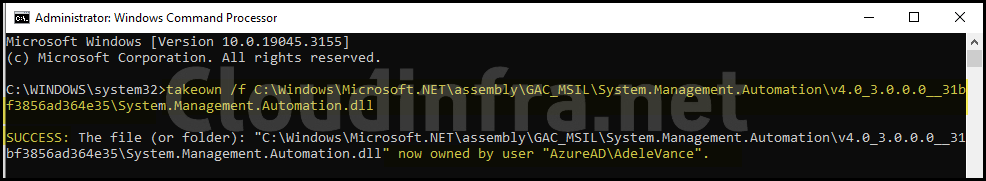
1. Take Ownership of System.Management.Automation.dll
Take Ownership of System.Management.Automation.dll file
takeown /f C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\System.Management.Automation\v4.0_3.0.0.0__31bf3856ad364e35\System.Management.Automation.dll
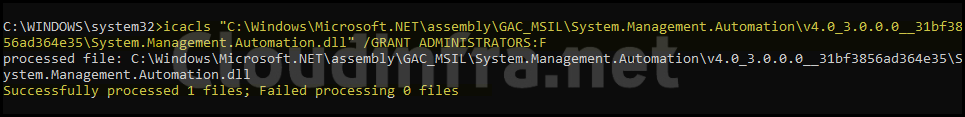
2. Grant Administrators full control of the System.Management.Automation.dll
Grant Administrators full control of the System.Management.Automation.dll
icacls "C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\System.Management.Automation\v4.0_3.0.0.0__31bf3856ad364e35\System.Management.Automation.dll" /GRANT ADMINISTRATORS:F
3. Copy System.Management.Automation.dll from a Working PC
- Now, log in on another Windows 10/11 device where Powershell works fine.
- Go to the folder C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\System.Management.Automation\v4.0_3.0.0.0__31bf3856ad364e35\ and copy System.Management.Automation.dll file.
- Now return to the device where Powershell is not working. Paste this file somewhere on the device, for example, C:\Temp.
- Open the Command prompt as administrator.
- Execute the below command to replace the faulty System.Management.Automation.dll file.
Execute this command to paste System.Management.Automation.dll file
copy C:\Temp\System.Management.Automation.dll "C:\Windows\Microsoft.NET\assembly\GAC_MSIL\System.Management.Automation\v4.0_3.0.0.0__31bf3856ad364e35\System.Management.Automation.dll"
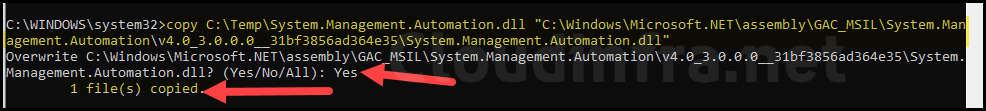
- Restart your device and test Powershell; this time, it should launch perfectly fine.
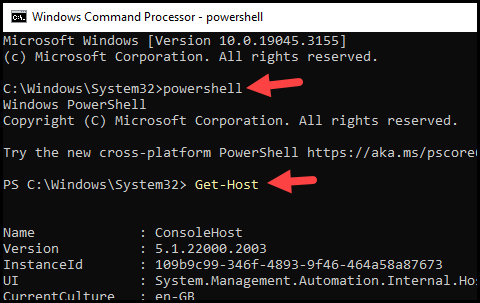
- Previously, there were issues when attempting to switch to the console within the Command Prompt. Those issues have also been resolved. You can initiate PowerShell from the Windows Command Prompt, which has been confirmed to work correctly after replacing the DLL file.
Other Solutions
While the provided solution addresses a specific error message, if you’re experiencing a similar issue where the PowerShell console crashes or behaves unexpectedly, there may be alternative solutions to explore.
1. Uninstall and Re-Install PowerShell
To resolve issues with a corrupted PowerShell feature, you can try uninstalling and reinstalling it, which should replace any corrupted files. You can do this through the command prompt or the GUI. Here are the steps:
Disable Powershell feature
Dism /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:"MicrosoftWindowsPowerShellV2Root"
Enable Powershell feature
Dism /online /Enable-Feature /FeatureName:"MicrosoftWindowsPowerShellV2Root"
To uninstall the PowerShell feature using the GUI, follow these steps:
- Press the Win + R to open the Run dialog box.
- Type appwiz.cpl and press Enter.
- Click the Turn Windows features on or off link on the left-hand side in the Programs and Features window.
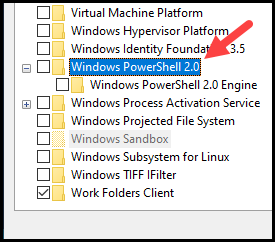
- Scroll down the list to locate Windows PowerShell 2.0.
- Uncheck the selection next to Windows PowerShell 2.0.
- Click OK to confirm and begin the uninstallation process.
- Restart your device after the feature is uninstalled.
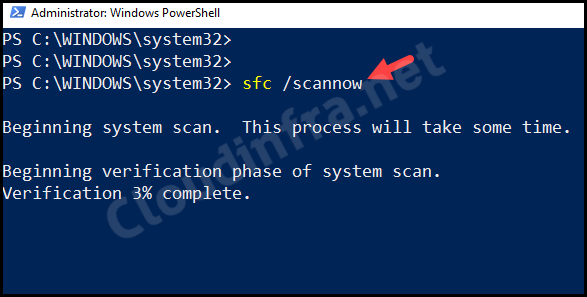
2. Run the System file checker tool
You can use the System File Checker (SFC) tool to address issues with corrupted system files. Here’s the process, which involves running the Deployment Image Servicing and Management (DISM) tool before using SFC:
Run DISM Tool:
- Open Command Prompt with administrator privileges.
- Type the following command and press Enter:
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth
Run SFC Tool:
- After the DISM tool has finished, run the System File Checker (SFC) tool.
- In the same Command Prompt window, enter the following command and press Enter:
sfc /scannow
Troubleshooting
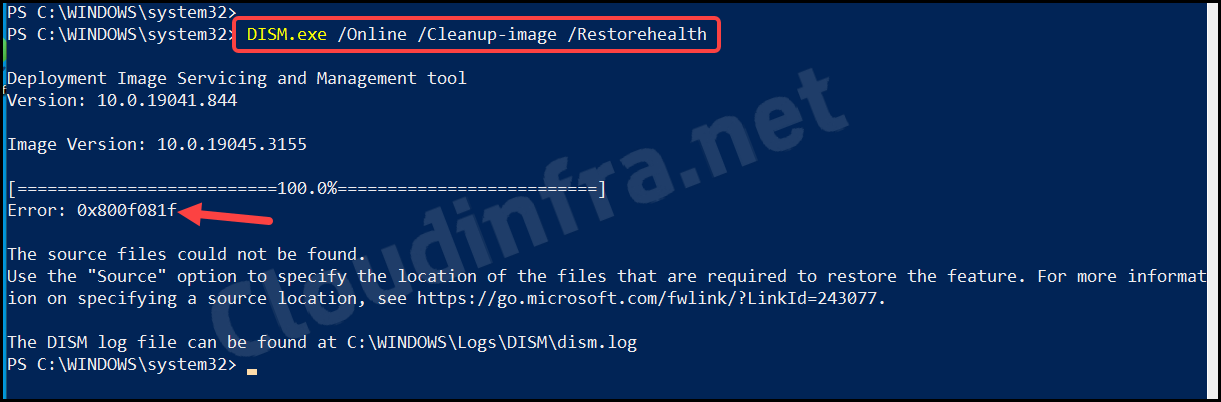
1. Error code: 0x800f081f
After executing the DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-image /Restorehealth command, you may get this error code.
The source files could not be found.
Note
Use the Source option to specify the location of the files that are required to restore the feature. For more information on specifying a source location, see https://go.microsoft.com/fwlink/?LinkId=243077.
This could be because of a lack of internet connection or a firewall issue. You could try an offline restore method by copying the Windows folder from a working Windows computer to a faulty computer and providing it as a source to restore the files.
DISM Offline Windows System files repair
DISM.exe /Online /Cleanup-Image /RestoreHealth /Source:C:\RepairSource\Windows /LimitAccess
The LimitAccess parameter in DISM instructs the tool not to check Windows Update or Windows Server Update Services for the capability source files.
After completing a Windows repair using DISM Command, run the System file checker tool to scan all protected system files and replace corrupted files with a cached copy in a compressed folder at C:\Windows\System32\dllcache.
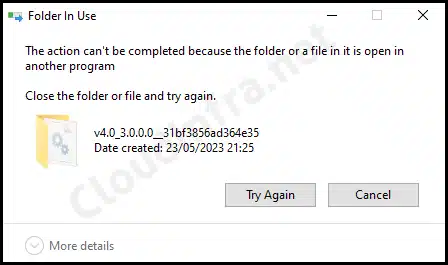
2. Error while Copying System.Management.Automation.dll
While it’s straightforward to copy the System.Management.Automation.dll file from a functioning Windows device, you might encounter the following error message when attempting to paste it onto the destination device: The action can’t be completed because the folder or a file in it is open in another program. Close the folder or file and try again.
This Issue can be resolved by taking ownership of the System.Management.Automation.dll file and grant administrators full control of the dll. The steps for taking ownership of this file are provided in the previous section of this post.
Conclusion
This blog post explores methods for resolving PowerShell launch errors, primarily by replacing corrupted DLL files. We’ve also discussed running the system checker tool to repair corrupted system files. If the issue persists despite following the steps outlined in this post, you can consider backing up your data and performing a device reset, which will replace and fix any corrupted files.